Important rules for grafting trees
Content:
Summer residents often think about how to increase the life and fruiting efficiency of plants, trees growing in their garden. One of the rather original ways is grafting trees. What are they really like and how are they used?
Grafting is the creation of a single organism through the mutual accretion of two plant species, which is achieved by transferring a specific part. This type of symbiosis begins to work when the root system of the first plant begins to supply and help the development of the second plant. Often this method is applied just to the second specially selected culture, which requires support in development and growth. Vaccination is carried out at the expense of improvised materials that play the role of fasteners.
Grafting trees: purpose
Is grafting fruit plants really worth it? As it turned out, only pluses and advantages come from this.
- Vaccination can help in obtaining a specific variety from another area and region, which would have to be looked for in gardening stores. It often happens that it is problematic to get a specific variety, in the same case you only need a cutting for subsequent accretion.
- Surprising as it may be, but grafting allows you to grow varieties of plants that initially simply would not have taken root in the area where the garden plot is located. The main thing is to create conditions, i.e. to graft them to frost-resistant varieties, then the plants brought, say, from the south will be protected from death and wilting.
- The ripening of the crop is significantly accelerated when using the grafting technology. If you are grafting on an adult tree, then in about 2-3 years you can expect a crop to appear, while the average period is from 5 to 15 years.
- If the plant has already been damaged mechanically or, say, by sunburn, then grafting can completely save the culture from death, so in this case it is not recommended to hesitate with a decision.
- Vaccination creates conditions for the prompt replacement of a poor and decaying variety with a more perfect one in terms of characteristics, fruiting and / or requiring less care costs.

- Ultimately, it is thanks to grafting that you can widely diversify crops in your garden without much effort and cost, while significantly saving the area for planting. After all, you can already get 3-4 varieties from just one tree, you must admit that it is much more convenient and cost-effective than planting all valuable space with trees of one variety.
Features and grafting algorithm
In all this interesting process, three main terms and concepts can be distinguished: scion, rootstock, cambium. Let's put each of them on the shelves in order to operate them competently in the future.
Graft - in fact, a part of that plant, which will later be used for engraftment on another, followed by joint fusion. Most often, some part of the stem, bud, etc. is used for the scion. It is important to know that in the future it will be responsible for the varietal characteristics of the final plant, and will occupy its upper part.
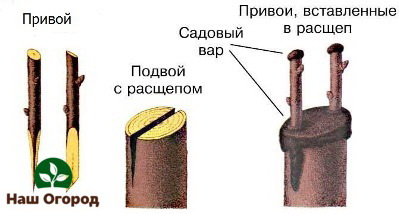
Rootstock - accordingly, that part of the plant, to which the graft will take root for subsequent accretion. According to its functions, being the lower part, it will be responsible for the distribution of power, resistance to climatic / weather conditions.
So, we can say that the scion and rootstock are key participants in the process, but what then is the so-called cambium?
Cambium - a thin layer of active cells, the location of which is characterized in the interval between wood and bast. The fact is that the whole process of grafting is due to the natural ability of trees to regenerate. Indeed, at the moment of accretion, specially made cuts on the scion and rootstock are superimposed on each other, as if uniting, and here the cambium already begins its work. Its layers connect and activate interaction with each other. Both plants, for their part, immediately try to heal the resulting wounds, which provokes the release of a special healing tissue called callus. Ultimately, after a while, a completely new conductive tissue is formed, which is the final result of the grafting procedure.
General rules
Of course, one should not try to create a "garden Frankenstein" by subjecting completely incompatible cultures to the process of growing together. Let's take a look at the general rules by which the selection of stock and scion follows:
- The stock, first of all, must be compatible and suitable for the scion. Otherwise, the crops will reject each other and the vaccination process can be considered a failure. Here, the already mentioned frost resistance, a strong root system and resistance to different levels of moisture, whether it is a lack or an excess of it, are noted.
- The choice of the scion should be treated with care, because parameters such as the quality of the fruits and their quantity will depend on it. The scion cuttings should be harvested in advance, for winter / spring grafting - in the fall, but in the summer, harvesting is allowed immediately before the procedure itself. The main thing is to look at the presence of already formed buds of the plant, otherwise the process of further growth is unlikely to turn into success.
Grafting of fruit plants and trees is a unique experiment and experience for summer residents who would like to grow a wide variety of crops in their garden, even in the smallest territories and plots.

