Gooseberry propagation: all methods
Content:
The article discusses in detail the reproduction of gooseberries in different ways, in different seasons.
The gooseberry is sometimes called the "northern grape". Its main distinguishing feature is good rooting. If a branch of a bush lies near the ground, then it will immediately begin to put down roots. Later, these roots from the adventitious passages go into their own root system. Thus, the gooseberry grows very quickly.
Gooseberries have unique breeding abilities, but experts still advise you to personally control the reproduction of the shrub. By monitoring the propagation of gooseberries, you will always be sure that new seedlings are of high quality.
Gooseberry propagation in different seasons
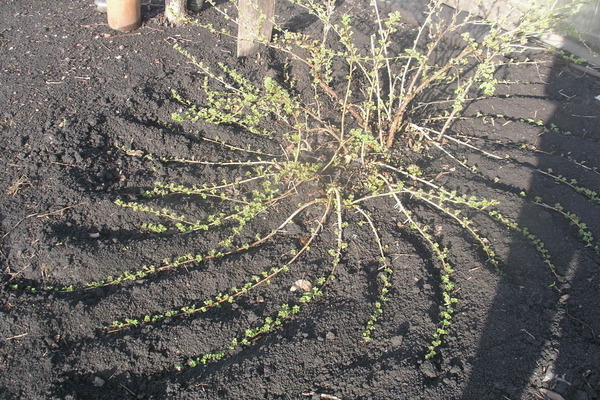

Gooseberry propagation
Before proceeding with reproduction, it is worth paying attention to the conditions that gooseberries require for root growth. First, a young plant is heat demanding. Secondly, he must have enough water.
Gooseberries can be propagated both in the spring and in the autumn. Usually the choice of the season depends on the chosen breeding method.
Let's say you decide to propagate gooseberries by layering. Spring is perfect for this method, preferably early. This is due to the fact that the active growing season will begin later.
Young cuttings, on the other hand, should be planted in the summer, at the beginning. The best month for still green cuttings is June. But the lignified ones fall on October.
A universal method in terms of the season is dividing the bush. This procedure can be carried out both in autumn and spring. Choosing when to divide the bush is best based on your region. If you live in warm regions in the south, then reproduction by division is possible from late summer to mid-autumn. In other areas with an average climate, division is carried out in the spring.
Another factor in choosing the type of breeding is the gooseberry variety. Each variety has its own characteristics that cannot be ignored. So, when propagating European varieties, layering should be used. Hybrid varieties are propagated by cuttings, green and mixed. The seeds are usually used to breed new varieties. But no one forbids amateurs to use them for garden experiments.
Gooseberry propagation: methods
Gooseberry propagation
As already mentioned, gooseberry roots grow very quickly and easily. It can be propagated at any time and from any part of the plant. The likelihood that the gooseberry will not take root is very small. In addition, he is very unpretentious. All this makes it a very affordable plant for beginners and those gardeners who do not want to spend a lot of time and effort for reproduction.
Gooseberry propagation by layering
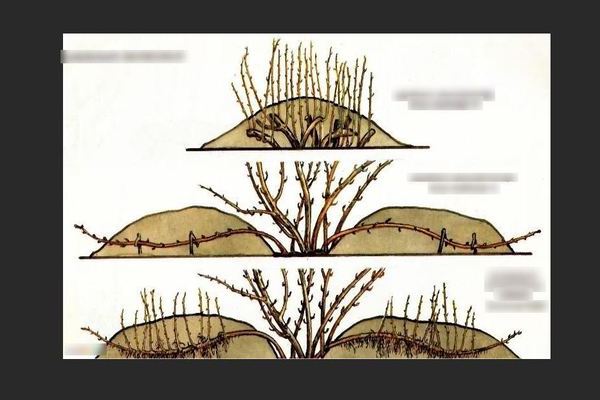
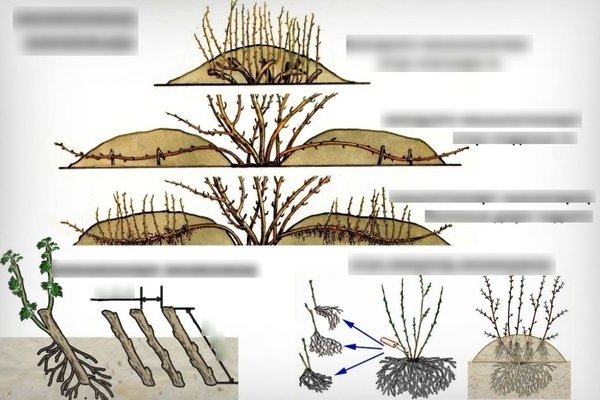
Gooseberry propagation by layering
The advantage of this method is its effectiveness: seedlings rarely take root. The most optimal time for such reproduction is October. However, the process of reproduction by layering is possible in the spring. The only difficulty is that it is necessary to be in time before the beginning of the sap flow period and to carry out reproduction in late March or early April. For propagation by layering, bushes over 3 years old and under 5 years old are best suited.
Before breeding begins, you need to pull out all the weeds near the shrub. After that, rotted manure is placed around the bush, digging in the ground 10 cm and then leveled.
It is best to prepare for gooseberry breeding a year before. A year before the intended breeding of gooseberries, branches are cut from the bush that are not suitable for layering.These include weak and diseased branches. After that, the gooseberry will grow new branches that will already be strong enough to be suitable for breeding.
Propagation by horizontal layers
For such reproduction, there is a simple plan of action:
1. Take a branched part of the bush. He should be already an adult and without diseased branches. You need to select several branches that grow close to the ground. The branches must be at least 1 year old and must not be more than 3 years old.
2. Selected branches must be shortened. You need to cut off the one-year increment. Thanks to this procedure, the buds grow better and, accordingly, stronger branches and a stronger root system are obtained.
3. After the first two steps, the branches are placed in oblong pits of shallow depth. After that, they are fixed. For fastening, you can use pins or any other hooks made of metal or wood.
4. The holes are covered with earth and watered. The first watering should be abundant. After that, the trenches with branches are covered with mulch.
5. Throughout the season, you need to make regular watering, as well as fertilize. Both mineral and organic fertilizers are suitable.
6. When the sprouts reach about 8cm, they are huddled, but not much. You will need to repeat this after two weeks after the first time.
7. When the branches have strong roots, they are cut off and dug up.
It is important to know that in order for the seedlings to grow faster, they need to be dug out together with a lump of earth.
The branches and roots of a young seedling must be tamed. After that, you need to plant a seedling so that it grows further. When a year has passed after planting, they will grow a normal seedling with several branches and good roots.
Propagation by vertical layers
Vertical layering is tedious if your plant is old. Then they are used to rejuvenate it.
1. The procedures should be carried out from the beginning of spring. All branches are pruned. Old branches are cut off completely. It is worth considering that branches are considered old, whose age is 2-3 years. Fresh branches should be cut only 2/3 of the entire length of the branch. All this is necessary so that the bush grows fresh branches more actively.
2. After the bush has given new branches, and they, in turn, have grown to 15 cm in length, you can proceed to the next step. The bush is huddled around, and then sprinkled with earth for about half.
3. All summer you need to watch the bush. If necessary, repeat the second step. If your shrub still needs hilling, then before re-carrying it, you need to water it well.
4. During the summer, the prospective cuttings are fed. A mineral solution for berry bushes is perfect for feeding.
5. In the middle of autumn, the layers that have already taken root are transplanted.
It is important to remember that the process of reproduction by layering consists in covering the branches with earth. That is, after that, the bush will not bear fruit for two years.
You need to make sure that there is space between the shoots, and that there is enough of it. This is especially important during the period of their growth. If this condition is not met, then the roots will become entangled with each other as they grow. They can intertwine to such an extent that during transplanting, they cannot be damaged. Since the shoots are young, damage to their roots can lead to their death.
Reproduction by arcuate layers
For most varieties of gooseberries, the following rule applies: the branches are usually in the shape of an arc. As already mentioned, gooseberries begin to take root with prolonged contact with the ground. Therefore, this method of reproduction occurs by itself, without human intervention. But if there is a desire to speed up the process and make it more efficient, you can carry out the following procedures:
1. In the place where the branch touches the ground, you should make a small hole.
2. In this hole you need to put a branch and fix it.
3. After that, fertilizer - humus is poured into the pit.After you have placed the fertilizer, form a small pile on top.
In the fall, in the middle, the branch should already take root well. Therefore, it is cut off from the very end and transplanted. If the roots are not strong enough, the seedlings can be grown. If all is well, plant permanently.
The only and main disadvantage of this method is that you only get one new bush.
Perennial branches
Gooseberries take root remarkably. Even old branches are not ignored by this rule. Usually such branches are cut, but after that they do not have to be thrown away. Old branches, like new ones, can be used for further propagation.
Breeding process by branches:
1. Cut off the old branch.
2. This branch is placed in a prepared hole or simply in the ground. Most of the branch should be underground.
3. Shoots on a branch must be cut off. This will give impetus to the growth of new ones.
4. In the summer, active watering should be observed. Also, during the season, you need to feed the plant several times. For fertilization, nitrophoska is used in a ratio of 20 mg per 1 sq. meter landings.
5. The transplant can be done after the new bushes are approximately 20 cm tall.
There is another way for those who are not very sure about the first one:
1. An old gooseberry bush 5 years old or more is taken. A branch is selected from it. The branch should not be sick or weak, and also grow from the edge of the bush.
2. The roots are cut at a depth of about 25 cm. This procedure is most conveniently done with a shovel. The bush is taken out of the ground. As already mentioned, it is important to keep the earth rooted. In this form, the bush is transplanted.
3. It is necessary to transplant into a pit made in advance. Then you need to fill it with earth and water it well.
Division
The division is applied most often to old bushes in order to save them. In this way, you will get young bushes from the old and dying.
The process of dividing the bush is as follows:
1. The bush is dug out of the ground. It is very important to do this carefully so as not to damage the roots of the bush.
2. The roots are cleaned from the soil that has adhered to them. All roots must be carefully examined for various diseases. If there are still diseased or injured roots, then they are cut off. The shoot that grew from these roots is also cut off.
3. Now consider the bush itself. You need to choose the youngest and not diseased branches. The roots of the branches must be strong. After that, the selected branches are cut off from the bush.
4. These branches are the seedlings that need to be transplanted.
Gooseberry propagation by cuttings
This method is not very suitable for beginners. However, he has a great advantage over others. By cuttings, you can get many young bushes at once.
Propagation by cuttings occurs in warm conditions. It can be a greenhouse or just a film on the bushes. Here comes up and the main disadvantage of propagation by cuttings. Not all bushes take root after transplanting from greenhouses and shelters. Therefore, this method is recommended for experienced gardeners. This is due to a sharp change in temperature conditions. To increase the likelihood of survival, you need to gradually prepare the plant for new conditions. To prevent the plant from dying, a few weeks before planting in another place, the film begins to be removed. They also lower humidity and make watering less frequent. It is important to do all this gradually.
It is very important to pay attention to the stage of development of the cuttings. It also directly affects whether the cuttings die during transplantation or not. If the cuttings are still green or already woody, then they will not take root well. Young cuttings can simply rot from moisture, and too old cuttings do not take root so well.
Green cuttings
Consider the features of planting young cuttings.
They are very finicky in terms of temperature conditions. In the daytime, the temperature should not be more than 23 degrees, and at night - 21 degrees. Also, it should not fall below 18 and 16 degrees, respectively.The temperature of the water is also important. The most optimal solution is watering with lukewarm water.
If the temperature in the greenhouse or under the film is more than 25 degrees, then the cuttings will simply rot.
In order to facilitate the creation of the desired temperature conditions, it is necessary to plant the cuttings in the summer. The beginning of summer, its first half, end of June - beginning of July is best suited.
The process of breeding gooseberries with young cuttings is as follows:
1. New growth is cut off from the bush. It is important to do this when the weather is right. It could be early morning, or it could be a humid, cold day.
2. The resulting shoot is divided into several parts. The length of the pieces should be from 8 to 15 cm. It is important to do this with a well-sharpened knife.
3. For active growth, the resulting cuttings are wiped with potassium permanganate. There is another option: put it in a growth stimulator for a day.
4. Cuttings are thoroughly washed with plain water. Planting is done in pots. The container for cuttings should always be small. To accelerate root growth, the planting material is covered with a film. You also need to ventilate them regularly.
5. When the cuttings take root, you can safely transplant them.
Lignified cuttings
Cuttings of this type can be prepared not only in spring but also in autumn. You always need to harvest a lot more cuttings than you need. For example, twice as much. This is due to the fact that not all cuttings take root.
The process of breeding gooseberries with wood cuttings is as follows:
1. If the harvesting of cuttings occurs in the fall, then you need to do this before planting. If in the spring, then until the buds swell. For cuttings, strong branches are taken, their upper part. Cuttings should be from 8 to 15 cm. If the cutting is taken from the bottom of the branch, then its probability of survival decreases.
2. Autumn cuttings are planted in the middle of the season. In the spring, on the contrary, at the beginning. It is important that the ground is already thawed. If you are not going to plant them soon, then you need to process them with growth stimulants. After processing, place in a wet piece of cloth, put in a bag or plastic wrap and place in a cool place. The bag or film should not completely insulate the cuttings to keep moisture inside.
3. Planting of cuttings occurs at an angle. The angle should be 45 degrees. The distance between plantings should be about 20 cm. The slope of the cuttings is necessary in order for the roots to grow faster.
4. When the cutting is already in the soil, it must be fixed and watered. You need to water slowly so as not to displace the stalk.
5. A 5 cm layer of mulch is placed around the seedling.
If the cuttings are planted in the fall, then during warm weather you need to loosen the ground around the cuttings.
If in winter the cuttings come out of the ground a little, then it's okay. Place them deeper and secure.
All summer you need to carefully monitor future bushes: fertilize, water and loosen the ground.
In any of the ways of rooting cuttings, it is important to know one feature. The ground should always be moist. Gradually, with the growth of cuttings, the moisture is reduced to that which stands in the open field.
Combined cuttings
What are called combined cuttings? This is a young green stalk, the lower part of which is already woody. Such cuttings come with a stand, with a heel and with a crutch.
The combined cutting is planted at the end of the spring season. The length of the shoots by that time should be about 6 cm.
If there is old wood on the handle, then it is less whimsical to the conditions. Therefore, such a stalk takes root much better.
Seeds
As already mentioned, seeds are an excellent option for breeding a new variety. This is due to the fact that bushes obtained from seeds do not carry the characteristics of the original bush.
Breeding process:
1. Take ripe gooseberries, take seeds from them. The seeds are placed in the sand, mixed thoroughly, placed in a container.
2. Before the cold weather sets in, a box or other container with seeds is placed half a meter into the ground and covered with earth from above to half the depth of the pit.
3.After the onset of spring, the contents of the container are sown in the greenhouse. Then you need to fertilize with a peat layer.
4. All summer long you need to carefully monitor the sprouts. They can be transplanted at the end of October.
Conclusion
Gooseberry propagation is a fairly simple process that any beginner can handle. All actions are very simple and do not require any special skills. It is worth paying attention to the season and variety of gooseberries when choosing a planting method. You also need to consider the number of desired bushes. To keep the new bush strong and healthy, you need to fertilize and water it regularly.
Gooseberry propagation

