With fruit trees on the "you".
Description of fruit trees: structure and activity
In order to grow certain plants, including trees, the summer resident should have an idea of what their structure is, what it is - after all, not only the ease of understanding their business depends on this, but also the aspects of care in handling in vegetation. Let's figure out exactly how fruit trees are arranged, and also consider the cycle of their life.
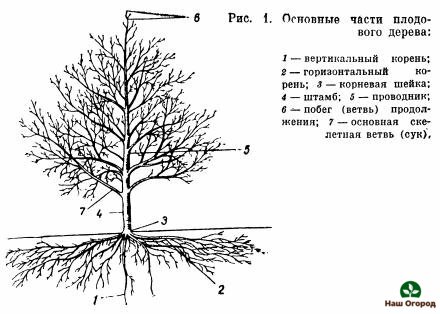
As you might guess, in fruit plants everything starts from the central organ - the root system. The main processes and functions are tied to it, which are realized further in the outer part of a plant, otherwise called aboveground. The transition between this part and the root system is referred to as the root collar.
The so-called aerial part of a fruit tree is a stem, a part of the trunk located from the root collar to the skeletal branch below, as well as the crown, in other words, a branched part of the tree located above. It is customary to call the leader the extension of the trunk above the trunk itself, and this part can also be called the central conductor. Skeletal branches of orders of the first, second, and so on depart from the central conductor. The intermediate branches are already located between the skeletal branches, hence the origin of their name.
In order to speed up the formation of the crown and simplify the whole process, it is recommended to leave only one branching order, while the second order, together with intermediate branches, is better placed in a horizontal position. They, in turn, are called semi-skeletal.
Semi-skeletal and skeletal branches are characterized by the presence on them of smaller, most often overgrown fruit branches. Unfortunately, their annual growth rate is rather short, and they themselves develop much weaker.
A stem that has grown and developed in a given vegetative period, on which there are already leaves, is called a shoot. It is also correct to denote annual growth with this term both in winter and summer seasons until the moment when new growths from the buds appear. When they bloom, the scales crumble, thereby forming traces at the base of future growth - these are the annual rings familiar to us. Thanks to the growth rings, you can almost accurately determine the age of the plant and its components - the branches.
Analyzing the types of shoots, it should be noted that they are both growth, that is, vegetative, and fruit - reproductive. Fruit buds differ in size from growth buds, because they are usually larger and rounded. Thus, it becomes quite easy to recognize them by their appearance already from the autumn season.
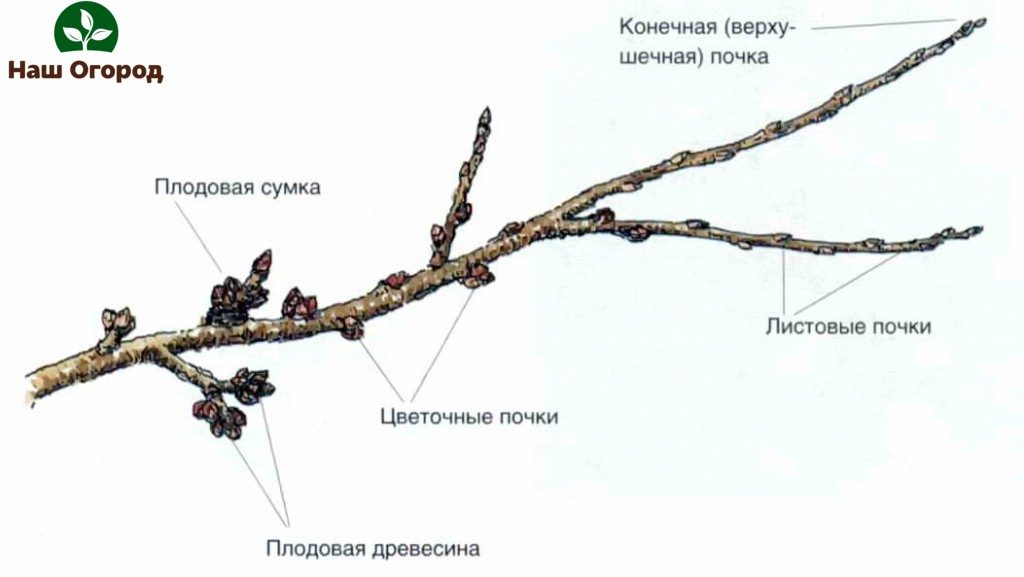
There are also strongly shortened shoots, called ringlets. These are a kind of fruit formations, presented with one well-developed bud located in the upper part, as well as with a rosette of leaves. You can also recognize the age of the ringlet, if a short-sized shoot with a rosette of leaves develops from the bud. Such a ringlet can be called biennial.
There are also parts such as a fruit twig and a spear. The first is nothing more than a small one-year branch, as a rule, slightly longer than 15 centimeters, differing in diameter and thinner in comparison with the growth one. It ends with a fruit bud. So, for example, these same fruit buds in apple varieties are located in the axils of the leaves of new shoots. Kopetso is another type of annual branch, its length varies on average from 5 to 12 centimeters.It differs in uniform, uniform thickness, as well as in the feature that it departs almost at a right angle from the main bearing branch. The fruit bud is also the culmination, although the spear, in turn, has lateral ones, but they most often remain underdeveloped.
The root system of fruit trees, being a key organ of life, is characterized by vertical and horizontal arrangement of roots. With a thorough development, the former can be called a pivot system. By location, horizontal roots are most often distributed in the upper layers of the soil, those that are considered the most fertile.
In describing fruit trees, attention should be paid to the roots. Young roots of the skeletal type, in turn, form a root lobe - a system of densely branched small roots, a feature of which is the presence of suction hairs - a tool designed to extract nutrient solutions from the soil. Active roots, of course, must have constant access to oxygen, otherwise their development can be considerably slowed down. It is they who provide, control the normal vital activity of the tree, as well as its leaves. Therefore, whenever you carry out the fertilization procedure, loosen the soil, know that you not only provide the tree with the necessary substances, but also provide significant support and assistance to its root system.
Trees are an amazing life form, representing a whole system of interconnected parts, which are assigned their functions and tasks. Don't assume that because trees are so strong and durable, they don't need much maintenance. Pay attention mainly to the root system of fruit plants, and then they will delight you with a rich harvest every new season!




