Effective methods of treatment of a beauty - Hoyi
Content:
Hoyu, like other crops, can infect both diseases and pests. To prevent this from happening, you need regular prevention and treatment of hoya.
About hoya diseases and hoya treatment
Excessive humidity and too low temperatures in the room can contribute to fungal infections such as gray mold and powdery mildew. They can easily be seen by gray or white bloom on foliage. Powdery mildew can be treated with chemicals, but gray rot can kill a plant in a matter of days.

If spots and seals appear on the foliage of the culture, then the hoya is probably a more viral infection. It is necessary to isolate the plant from its neighbors and observe. If you do not see any improvement, then the flower will have to be destroyed, because viral diseases are practically not cured.
If the stems and shoots become soft and a sticky, foul-smelling liquid begins to ooze from them, then the plant is likely to have a bacterial disease. It is necessary to spray, and destroy the affected parts of the plant.
Hoya can also get sick with non-communicable diseases, usually they arise due to insufficient care and poor conditions within the room.
Hoya treatment for possible diseases
Spots on foliage. They can appear from excess sunlight, or from watering with too cold water or from overfeeding with mineral fertilizers.
Deformation of the leaves. The foliage of the plant may begin to lose color, shrink, or dry out. This happens due to excess sunlight, or from low room temperature, and watering can also affect this.
Stunted growth... Insufficient development in growth and loss of color can be triggered by a lack of nitrogen fertilizers in the soil.
Falling foliage. Leaves can begin to die off both from the abundance of water and from its lack. It can also happen when the air in the room is hot and dry.
Redness of foliage. The leaves of the plant can begin to turn red due to excessively high air temperatures, as well as from a lot of sunlight.
Reset buds and flowers. Hoya will shed its buds and flowers, due to a change in its habitat. This is also due to constant excessively abundant watering, or from a lack of light.
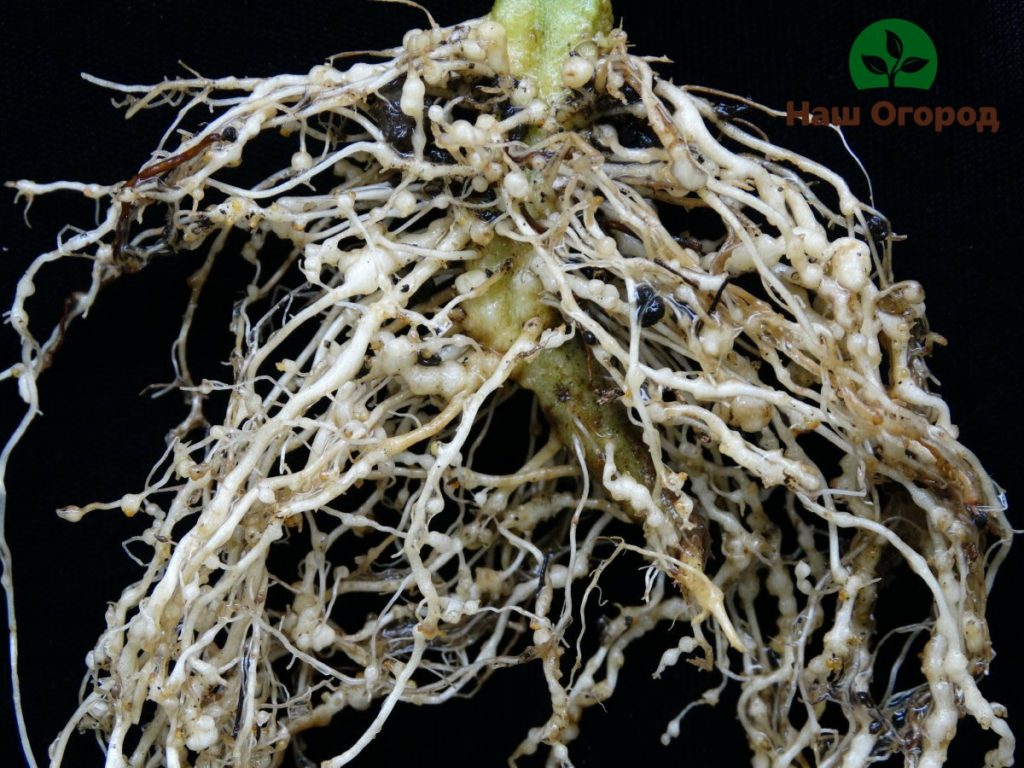
Rotting of the root system. This is due to excessive moisture and poor soil drainage. If the roots start to rot, then the plant risks dying.
Insufficient flowering. This can happen due to lack of light. This culture will not bloom without proper sunlight. Also, the hoya should have a good rest in the winter, that is, be at rest. At this time, you should provide her with a lower air temperature, reduce the frequency of watering and abandon fertilizers for two to three months.
Yellow foliage and poor development of young shoots. This is mainly due to too low temperature conditions.
Hoya pests
The main enemy of this ampelous vine is the root nematode. In its presence, the plant slows down in growth, and first yellow and then brown parts are formed on the root system, in time they die off. Spraying and rinsing the roots with hot water helps well in the fight. Excessively affected areas of the root system are cut off. The culture itself must be transplanted into another, disinfected pot with nutrient soil.
Also, although rarely, the plant can be attacked by: aphids, spider mites and mealybugs.It will be easy to understand this from the outward appearance of the culture. Hoya will begin to lose the bright color of its leaves, the foliage itself will turn yellow and die off. There will also be a slowdown in growth development, the buds will not open, and the flowers will become sticky due to pest secretions. A thorough examination should be carried out, especially in the spring, when young shoots begin to grow. If you find pests, then you need to place the plant under a warm shower and just wash off all the insects. After the plant dries up, you need to spray. If after a week the parasites have not died, then it is worth treating the plant again until the plant is completely free of them.

