How to propagate an apple tree
Content:
Apple trees are perhaps the most numerous inhabitants of Russian gardens. And every single amateur gardener, no doubt, has his own favorite apple variety that he would like to have on his farm. And sometimes you need to update the plantings, but you don't want to lose the apple varieties dear to your heart. Then the gardener is faced with the question of how to propagate an apple tree? In this article, we will look at the most popular ways to propagate apple trees, noting the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
How to propagate an apple tree with seeds
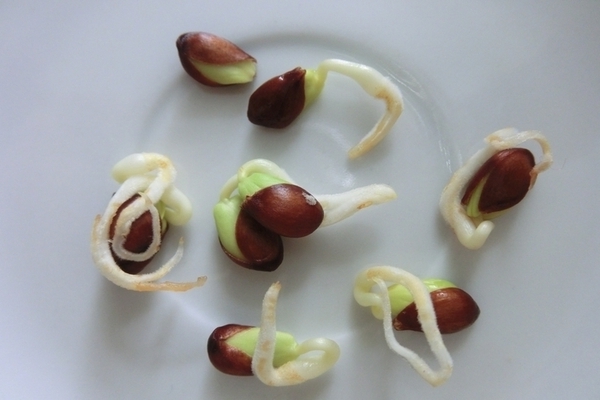

This method is not very popular with amateur gardeners. Rather, it is used by professional breeders when new varieties are being developed. This is due to the fact that in the overwhelming majority of cases, a plant that has grown from seeds does not receive maternal characteristics, and will, rather, be a wild apple tree.
Such a plant is possible and will bear fruit, but it is impossible to predict what the apples will taste like. It is advisable to use such trees as a stock, but they will enter fruiting in 7-9 years. But such seed stocks grow tall enough, they are not whimsical and high-yielding.
To obtain seeds with as large cultural traits as possible, you need to take the flowers of two plants and "exchange" their pollen. The seeds obtained from this mixing will receive the characteristics of both plants. However, it is a pity, but not all characteristics of the "parental" plants are preserved, and the process of pollination is quite laborious. Therefore, using this method of reproduction of apple trees in your area most likely does not make sense.
How to propagate an apple tree by cuttings
This method can be divided into two subspecies
Using cuttings as a scion
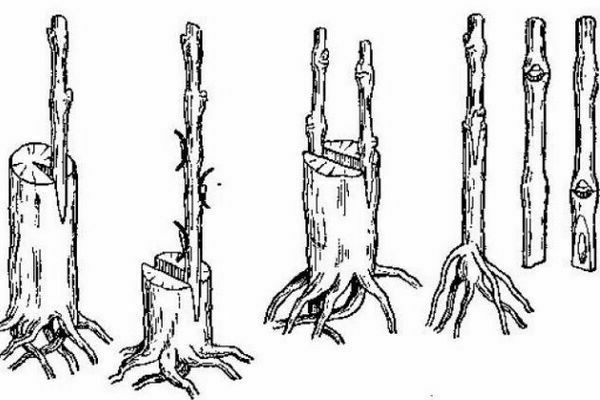
To do this, you need cuttings harvested from young shoots (first year). They are cut from the tree on the very day the grafting is scheduled. In the future, the cuttings will not be usable. Therefore, cuttings are taken exactly as much as you plan to use that day.
All foliage must be removed from the cuttings and grafted to the roots of the stock. In this case, the vaccination site does not need to be sprinkled with earth too much. Otherwise, the cutting may give independent roots and the grafting will be unsuccessful.
In this case, wilds are the best suited as a stock. They are unpretentious, adapted to local climatic conditions, tolerate low negative temperatures well. In order to choose a stock, you need to consider:
- if the stock is not tall, then it is better to graft cuttings of columnar apple trees to it.
- it is better to graft an apple-tree stalk of high varieties to a stock grown from seeds.
In the northern regions of our country, where there are long and harsh winters, which entail frequent freezing of apple trees, grafting to a dwarf stock is also possible.
Such rootstocks are grown in specialized nurseries. They are subdivided into superdwarfs, dwarfs, semi-dwarfs. When planting such a rootstock, make sure that the root collar is 4-5 cm above ground level. In this case, the vaccination site will be located a few more centimeters higher. The roots of dwarf apple trees need to be deepened more than usual, and the apple tree itself must be tied to a support.
It is necessary to vaccinate with a handle in the spring, and with a bud (by budding) at the end of summer.
The qualities of apple trees grafted onto a dwarf stock will depend on the characteristics of both trees.However, the main qualities inherent in most of them can be distinguished: it is good fruiting and a compact crown.
Among disadvantagesinherent in apple trees grown on such a rootstock:
- poorly developed roots;
- low resistance to drought;
- exactingness to the composition of the soil;
- increased fragility of wood.
But if the groundwater in your garden is very close to the ground, you can grow a whole garden of dwarf apple trees.
Propagation by root cuttings
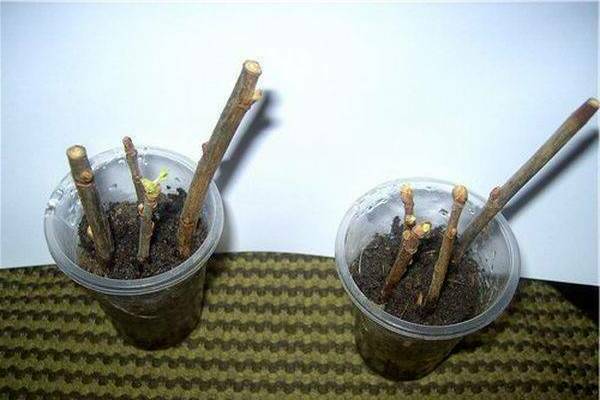

This method is vegetative and allows you to preserve all the characteristics of the mother plant. Thus, apple trees grown from root cuttings do not need grafting.
Planting material for this method is prepared in the spring, even before the buds bloom, or in the fall. Cuttings should be about 20 cm long. Prepared cuttings are planted in the ground (in furrows) to a depth of 2-3 cm from the cut. At the same time, a distance between plants of 25-30 cm is observed, and between rows of 1 m.
After planting, it is better to shade the seedlings slightly, and cover the ground with a layer of mulch, for example, humus. Remember to water your plantings regularly. Rooted seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place in the fall.
Is it possible to propagate an apple tree by root suckers
This method is not very popular, since only rootstock grows from root suckers, onto which the variety you like is grafted into in the future.
In order to get root suckers, you need to choose a mother tree. It should be young and healthy enough with good fruiting. The selected tree is cut a little and dug in, covering with soil. After a while, basal processes appear. The offspring that are at some distance from the mother tree are considered the most suitable for transplantation.
You can separate young offspring and plant them in a permanent place at the age of 1-2 years in spring or autumn. Only root suckers with developed roots are suitable for transplantation.
Among the disadvantages of this method, it should be noted that it greatly weakens the mother tree, and the offspring do not take root well in the new place. And among the advantages, one can single out the fact that the method of root offspring allows you to get several seedlings of the variety you are interested in at once.
How to propagate an apple tree by layering
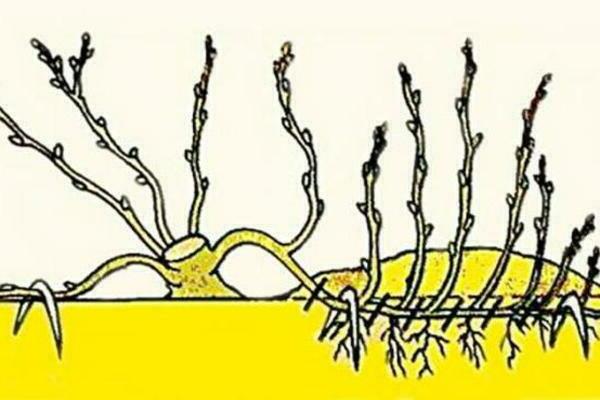
This method is essentially similar to shrub propagation by bending and rooting branches. The scheme of action in this case is approximately the same. The branches of the first year of life are cleared of leaves at a height of 25-30 cm from the top. In the place where the shoot will touch the ground, make a hole, fill it with a mixture of sand and garden soil, bend the branch and fix it. The crown of the shoot must be tied up so that the formation of the seedling goes vertically.
After the cutter has developed its own root system (as a rule, this happens during the summer months), it can be divided with the mother plant and planted in a permanent place. Or you can first place the cuttings that gave the root in a flower pot and grow at home for some time. Then the process of plant acclimatization in the future will be much easier.
The disadvantage of this method is the fact that, unlike shrubs, tree branches grow high from the ground, which makes them difficult to bend down. In addition, the total time from bending down to rooting already in a permanent place of a new plant takes about six months.
From the pros - you can bend the branches for rooting not only in spring, but throughout the year (with the exception of the flowering period and hot and dry days). In addition, the resulting seedling does not need grafting and carries all the qualities of the mother plant.
Propagating a tree with a broken branch
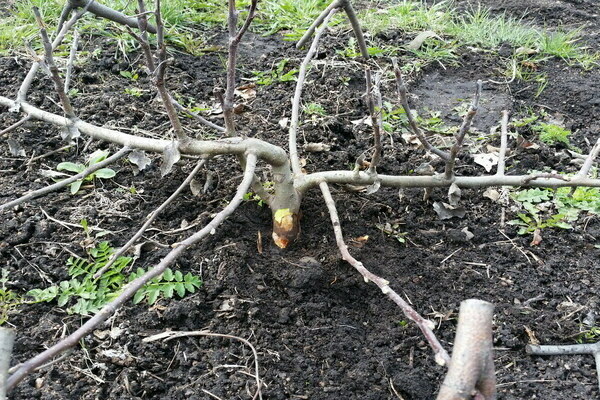

Basically, this is the same method of propagation by layering. It can be carried out in two directions.
In the first case, shoots of the first year of life are taken and buried in the ground, deepening by 10 cm so that the above-ground part is 30-40 cm in length.The branch is tied to a support. During the entire growth period, the seedling is watered and also weeded. After about a year, the branch will take root and can be planted in a permanent place (it is better to do this in the fall).
In the second case, the bark is cut off on the selected branch at a distance of 10 cm from the growth point, and the cut site is treated with a root formation stimulator. Then the cut is wrapped with a material that holds moisture well (moss, for example), and on top with a film. After root formation, the branch can be transplanted to a permanent location.
Saplings obtained in this way retain all the characteristics of the mother plant, and fruiting occurs in 3-4 years.
Cloning as a way to propagate an apple tree
This method is gaining more and more popularity.
Within the laboratory, cloning is carried out by placing cells in a special nutrient medium. Then these cells are affected by a certain set of hormones. As a result, a clone grows - an exact copy of the mother plant.
It only takes one winter to grow an apple tree. And in the spring, the apple tree can be planted in the ground. At the same time, the number of copies that can be grown as a clone is not limited by anything. The disadvantages of this young method are its high cost, as well as a high probability that the new plant will be hard and for a long time to “overload”, since it was grown under sterile conditions and lacks immunity.
At home, cloning is vegetative propagation that preserves all the varietal properties of the mother trees. Cloning by root suckers is possible. They are easily separated from the mother plant and have a high survival rate. The resulting trees begin to bear fruit after 4 years and give good yields.
Rooting of low-growing branches is also possible. To do this, under the branch that you plan to root, you can put a container with soil. Scratches are made on the bark of the selected branch, in a place determined for the development of the root system. These scratches are treated with a root formation stimulator, and then the branch is bent to a container with soil, fixed and covered with earth. As a result, roots should form, this will be the cloned layer.
How to propagate an apple tree with air layers
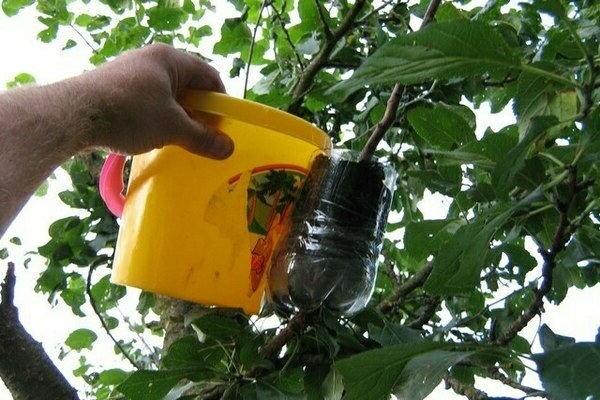

The most widespread method of breeding apple trees. To use it, you need lignified shoots. At a height of 20-30 cm from the point of growth of the shoot, you need to remove all the foliage and cut the bark a little in a circle. The cut is treated with a root formation stimulator, wrapped with a material that retains moisture (moss is well suited), and on top with a film or insulating tape. Over time, roots will form at the cut site. And the seedling can be separated from the mother tree and planted in the ground.
In conclusion, it must be said that it is not so difficult to propagate an apple tree of a favorite variety. In addition, as described above, for this it is not at all necessary to do time-consuming and requiring a lot of experience in vaccinations. Just choose one of the more suitable vegetative methods for you and go for it!

