Diseases of carrots: photo, description and treatment
Content:
The article presents carrot diseases: photo, description and treatment.
Carrots are one of the healthiest vegetables, full of nutrients and vitamins. No wonder he found his place in almost every cuisine in the world, in most of the dishes on our tables: in soups, salads and even juices.
Carrots are a low-calorie product and truly healthy. Not surprisingly, many people want to grow it in their garden.
However, unfortunately, we do not always get the desired amount of the crop. One of the main reasons for this is the diseases that every plant is susceptible to, and carrots are no exception.
After reading this article, you will learn to recognize and, most importantly, prevent many diseases by bringing fertility to your garden.
Diseases of carrots: variegated dwarfism
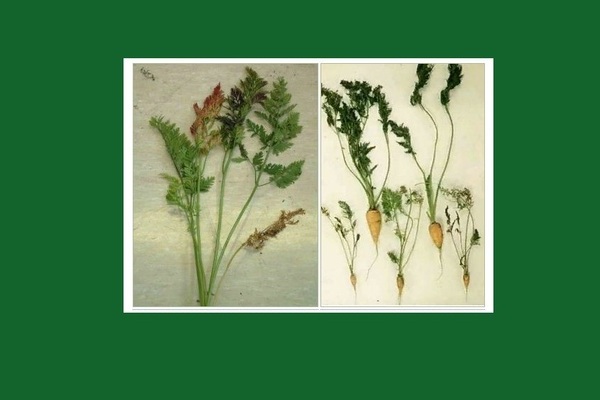

Diseases of carrots: variegated dwarfism
Description of the disease. Variegated dwarfism is a viral disease of carrots that causes, as you might guess, dwarfism of leaves and fruit. The virus infects the plant with the help of the willow-carrot aphid. Where wild or cultivated carrots are constantly growing, the aphid, together with the virus, hibernates right on it. As a result, at the very beginning of the growing season, the virus wakes up and infects crops of carrots and parsley. In colder places, infected aphids overwinter on fireweed, and only after feeding on an infected host plant does it become a source of disease.
Diseased carrots begin to change from the leaves. Their length is significantly reduced, and the shape of the petiole begins to bend unnaturally. After that, the leaves begin to change their color. Fancy patterns of red, light green, dark green and even black colors begin to appear on them. If the carrots have been infected too much by the virus, the foliage will stop developing altogether, which will be the first herald of the loss of the entire crop.
Unpleasant changes also begin to occur at the root. Root hairs appear, stopping the formation and growth of root crops. After this, premature lignification begins.
Outwardly, motley dwarfism is similar to a lack of nitrogen and potassium: disorderly mottling and eerie redness appear along the edges.
Description of the causative agent of the disease. There are two main pathogens of variegated dwarfism: Carrot mottle virus and Carrot red leaf virus. They are transmitted, as already mentioned, through aphids and nothing else. In an infected organism, the virus can exist for an extremely long time, posing a danger even after the death of the carrier. Both viruses are small: the diameters of their virions are 52 nm. and 25 nm. respectively. After infecting the host, they attack the phloem cells and those that are next to them, causing disease.
Disease protection measures. The best way to protect your crops from this terrible scourge is to try to eradicate aphids in the early stages of carrot growth to prevent possible infestation.
Diseases of carrots: photo description of black rot (alternaria)
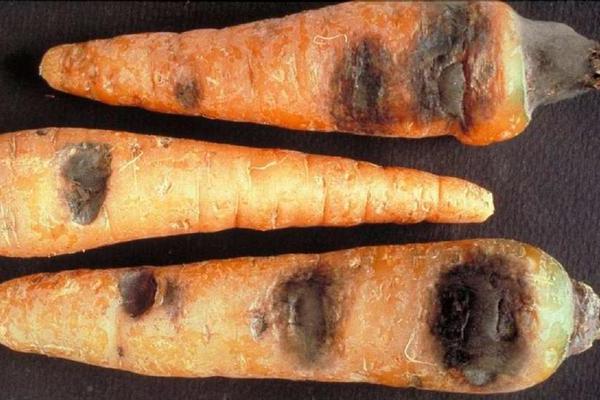

Diseases of carrots: photo description of black rot (alternaria)
Description of the disease. Black rot is a fungal disease that can destroy young seedlings already at the stage of 3-4 leaves and even earlier - even during the germination phase. After that, the disease will slowly dry up the leaves, as a result of which they will die off, which will rapidly diminish the harvest.In addition, black rot of root crops can develop directly during storage of carrots. Those fruits that have any external defects or damage first. Not only that, as a result, a significant part of the crop will die, so what remains of it will lose any digestible presentation. Due to a particularly strong infection by the spring, all root crops, without exception, will be completely or partially affected by this destructive fungus, because the infection comes, first of all, from the soil and seeds, where, by the way, it can remain indecently long for 8 years.
It is not difficult to recognize the disease. During storage, a gray mold-like plaque appears on the carrot roots. On the root crops themselves, distinctly visible black dry spots appear, somewhat similar to dents. They are most often found on the top of the fruit.
Description of the causative agent of the disease. The fungus that causes black rot is extremely widespread. It is difficult to find a place where gardeners would not have problems with it. The fungus has a standard spore size and brown or brown conidia. The most dangerous mushroom is in its usual environment: at a temperature of 22-25 ° C and with air humidity above normal.
It is believed that, in addition to carrots, this fungus also affects parsley, celery and other umbrella crops. But this is not entirely true, because their diseases are caused by extremely similar, however, nevertheless, other fungi.
Disease protection measures. One of the best ways to protect your crop from black rot is through proper farming techniques. The more attention and caution you take in caring for your site, the less often any diseases will visit it, and black rot is no exception.
Also, before planting and before sending carrots for storage, you should carefully select healthy roots. Storage should only take place in a room with a temperature of 0-1 ° C and with 80-85% humidity.
It is important not to forget to weed out weeds, because they are also carriers of this unpleasant disease. It is also important after harvest to destroy any residues that may still contain live pathogens.
If you want to 100% protect yourself and your crop, buy varieties resistant to Alternaria and monitor them with the same attention as for ordinary carrots. After all, their resistance does not make carrots immortal.
A few more words about storing carrots. To prevent the development of black rot, we recommend using the biological preparation "Fitosporin-M". For 1 liter. 100 ml of water is consumed. funds. After processing, do not forget to dry the roots dry.
In addition, there are hundreds of fungicides that are used to protect carrots from black rot. An excellent example is foundazol - a drug that protects the crop not only from black, but also from white rot, as well as from phomosis. For preparing a solution of 10 kg. water is diluted with 20 gr. active substance. Carrots must be placed in the resulting solution, then dried and, finally, sent for storage. Also, instead of foundation, it is permissible to use an old remedy called "Rovral"
In Europe, a remedy called Prozaro has long been used to treat black rot, but in the Russian Federation it has so far been used only for cereals.
Diseases of carrots: photo, description and treatment of soft bacterial rot
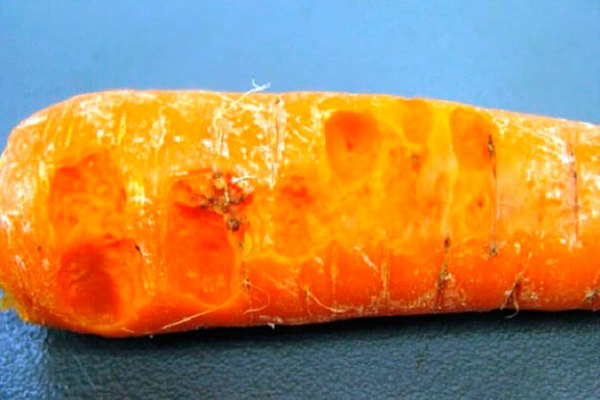
Diseases of carrots: photo, description and treatment of soft bacterial rot
Description of the disease. Carrots of the first and second years are susceptible to this disease. Infection leads to the inevitable death of leaves and subsequent decay of the fruit underground or in a warehouse.
The disease is especially contagious at high temperatures and high humidity. However, the bacillus cannot withstand too extreme conditions. Its maximum limit is 37 ° С.
The carrier of the infection is the Erwinia carotovora microbe, which infects carrots at the stage of growth.Carrots can be infected both directly through the soil and through insects (flies, caterpillars, etc.). The decay itself begins already in the warehouse and leads to extremely disastrous consequences. Small white growths begin to appear on the root crop. They look harmless, but over time they grow and develop into dark, solid tumors up to 7 cm in size. Their nature is very similar to cancer: instead of killing the cells of the fetus, the disease causes them to divide randomly. If the infected carrots are not removed from the soil in time, the growths will completely collapse, making the soil unsuitable for the growth of carrot plants for a long time.
If suddenly a tumor covers the entire root of a carrot, it will absorb a lot of nutrients and further contaminate the soil in which your future vegetables have yet to grow.
Protective measures against disease. The only sure way to protect your plantings from bacterial cancer one hundred percent is to buy disease-resistant varieties. Unfortunately, there is no way to completely protect yourself from such a dangerous invisible enemy as bacteria. However, if possible, try to disinfect your soil and clean it of all kinds of insects and pests. It is also possible to use various chemical and biopathogenic drugs, but this is not so simple, because it requires an extremely precisely calibrated dose and composition for your specific situation.
Carrot Diseases: Carrot Jaundice Treatment
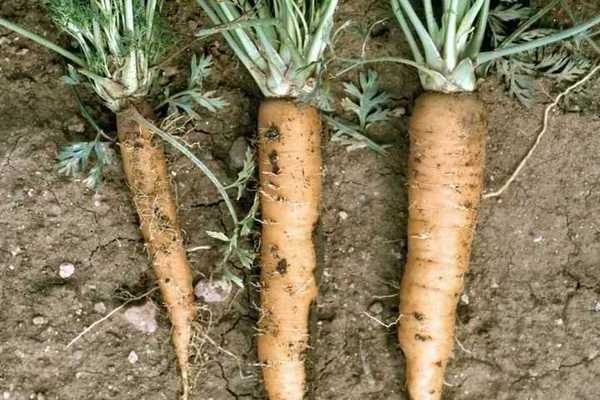

Description of the disease. Carrots of the first and second years are most often infected with this disease. Usually, the disease occurs during the appearance of the first shoots. Subsequently, the root crops do not take on the best appearance and are extremely poorly stored. Other crops are also susceptible to the disease, as well as flowers and weeds that exhibit similar symptoms after infection.
The disease spreads from a diseased plant to a healthy one, and the spread has nothing to do with physical damage to root crops. Also, carrots cannot be infected with jaundice through the seeds of diseased fruits.
After some time after the disease, the carrot leaves begin to turn noticeably yellow, and then completely acquire a burgundy color.
From the top of the fruit, small, weak shoots begin to sprout, resulting in the so-called "Witch's Broom". The plant stops developing and begins to grow overgrown with root hairs and small lateral roots. Since the root crop stops developing, its gradual untimely lignification begins.
Description of the causative agent of the disease. The pathogen overwinters in the bodies of infected cicadas, the roots of old infected plants, and in weeds. Also, do not forget that infected parsley planted nearby can become a source of danger.
Protective measures against disease. As is the case with many diseases on this list, proper farming practices are an important element of protecting your site. Also, do not forget that some varieties have developed immunity to this disease. However, do not forget to ensure that the carrots are isolated from infected plants, as well as that your garden is not terrorized by unwanted insects and weeds, because they are no less dangerous than direct contact with a diseased plant.
Carrot scab
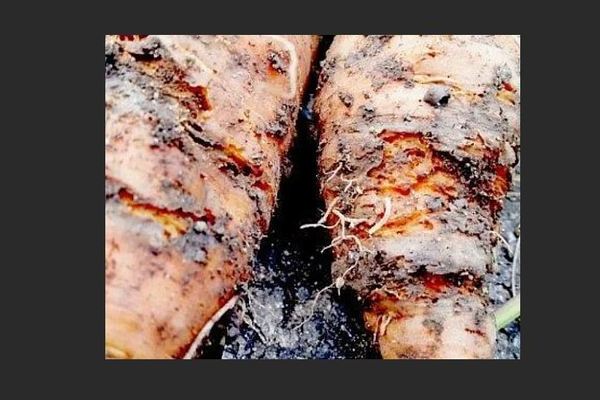

Description of the disease. The disease begins to affect the roots from the phase of three true leaves. It is especially "voracious" in unusually dry weather. Root crops that are unlucky enough to be affected by scab lose their beauty and become an easy target for wet bacterial rot in the warehouse. In addition to carrots, the scab pathogen also infects many other crops and flowers, so you may not want to plant them side by side when planning your next planting.
Over time, woody growths appear on the surface of the infected root crop, similar to the bark of a cork tree. They quite often grow across the carrot, encircling it like rings.
Protective measures against disease. Potash fertilizer and lime soil can serve you well in fighting this disease. Also, do not forget that this disease is not unique to carrots, and you should be especially careful when checking nearby planted beets, turnips or radishes for scab.
Diseases of carrots: treatment of root rot
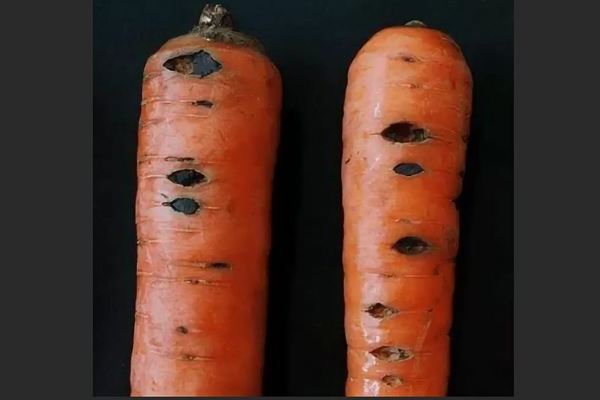

Description of the disease. Pit rot is one of the most common carrot diseases in the world. This disease is caused by fungi of the genus Pithyum, which, in fact, are countless. If the infection is very serious, up to half of the entire crop can die.
The infection is very fond of the usual warm weather with constantly high humidity, often accompanying heavy rains. Also, factors in the rapid development of infection can be an overestimated acidity of the soil, an excessive amount of nitrogen fertilizers and the use of not rotted manure fertilizer. The disease spreads through the soil due to soil nematodes.
Pit rot primarily causes seed rot in carrots, as well as weakening and premature death of seedlings. Those seedlings that still survived stop developing, and the roots lose their presentation. Their surface is dotted with soft dark spots, which later turn into cracks. They can become a focus of suppuration. Such carrots can be safely thrown away.
This disease in its early stages is very similar to phomosis and atternariasis.
Description of the causative agent of the disease. All types of Pithyum fungi live in the ground, feeding on the roots of seedlings infected with them. They have special organs adapted to penetrate carrots. After the mushroom is inside, it begins to slowly but surely destroy the tissues of the root crop from the inside. In the dead areas, new sporangia appear, which not only infect the roots of other fruits, but also remain in the soil for a long time after the carrots are removed.
Protective measures against disease. We never tire of repeating that the best prevention for protection against any plant disease is, first of all, correct agricultural technology. And also do not forget that there are special varieties and hybrid species that can easily resist this disease. If the soil is already infected with fungi, and you want to clean it, it is recommended to completely disinfect it and resume sowing only after 4 years.
Brown spot
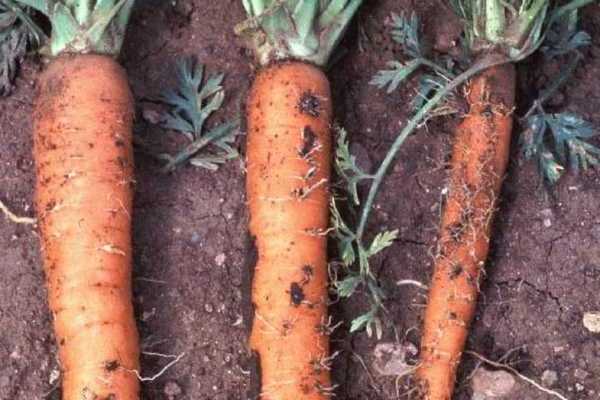

Description of the disease. The causative agent of the disease is also a fungus, known to gardeners as a leaf pathogen. However, paying attention to its destructive effect on the leaves, they often forget about the equally destructive effect on the root crop and causing rot in it. It appears as small, bright brown spots. The border of healthy and dying tissue is clear, as in a wound, and decay penetrates deep into the pulp.
The factors that accelerate the disease are windiness, excessive humidity and prolonged heat. With prolonged illness, you can lose a huge proportion of the crop.
Like many fungal diseases, brown spot causes rotting of the root crop underground and directly during storage. Over time, the rot makes its way deeper and deeper, until it completely destroys the root crop.
Description of the causative agent of the disease. All mushrooms of the brown spice species live all over the world and have similar conditions for rapid development and infection. Mushrooms spread in the soil through the roots. They persist in the soil for an extremely long time. Depending on how severe the infestation is, brown spot kills between 50% and 60% of the crop. Undead fruits lose their nutritional and external qualities, their weight and the sugars they contain. In addition, it is incredibly difficult to remove infected carrots without infecting the soil: the carrots get stuck in it.For gardeners, this is one of the worst diseases of carrots, as it deprives the garden of productivity for a very long time.
Disease control measures. Previously, in the fight against brown spot, gardeners preferred to use a product called "Rovral". Nowadays, biofungicides "Falcon" and "Prozaro" are considered to be extremely effective drugs. Unfortunately, they are not registered. Also, do not forget about the correct agricultural technology and about species and hybrids resistant to this disease.
In addition, if you want to plant carrots during the growing season or lay them in storage, you should take care of treating them with a biofungicide.
Diseases of carrots: treatment of fusarium
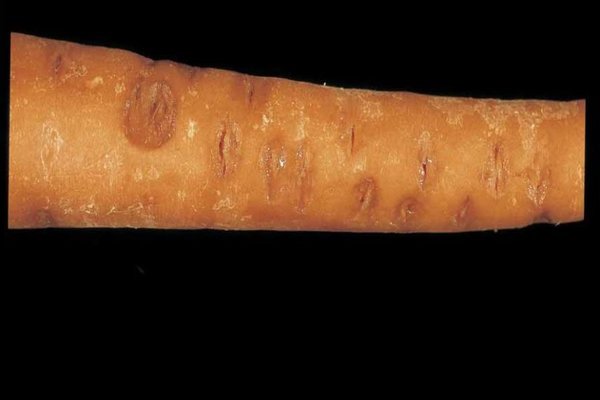

Description of the disease. This disease can overtake your carrots in both spring and summer. The fungi, which are the causative agents of this disease, not only attack the roots, but also cause the entire plant to wilt. These mushrooms enter carrots by penetrating a healthy root. There is another way: the infection can enter the plant through its cotyledons. The roots are the first to suffer from the penetration of the disease into the carrot. They are the first to start to rot, depriving carrots of their ability to reproduce effectively. The seeds of infected plants form weak and soft. This significantly affects the yield of carrots for the worse.
However, these mushrooms do the most damage during storage. Moreover, the older the root crop, the less resistant it is to disease. This is due to the fact that with age, their ability to accumulate protective compounds decreases. In addition, the age of the root vegetable also depends on how the fungus will infect it.
Fungi-causative agents of infection cause dry growths to appear on the surface of the root crop. Gradually, the rot progresses and covers the entire carrot down to the root, in a sense, "mummifying" it.
Most often, infection occurs in the warm autumn, when it is most often damaged. The fungus makes its way into the open "wounds" of the carrot and begins to poison it from the inside.
In the case of an attack by fungi on young carrots, the symptoms begin with a brown staining of the leaf roots. After that, the leaves wither and die. After that, the brown infection spreads to the top of the carrot, causing rotting and all the symptoms described above.
If the plant was infected in the first year of life, the root collar begins to suffer from the disease first. Its tissues, under the influence of substances secreted by the fungus, soften and die. The sprouts do not have time to grow enough to break through to the surface. Seedlings also stop developing, gradually turn yellow and also die. If the damage was not too intense, the plant has a chance of survival, but it will certainly lose any presentation, as well as the ability to absorb water, which will significantly impair the taste of the fruit.
If a more mature plant has been infected, Fusarium will not make it so easy to find out about itself. The roots will develop more slowly, and a subtle yellowness will appear on the tips of the leaves. Slowly and gradually, the leaf will still dry out, but such critical consequences, as in young plants, should definitely not be expected.
Root crops infected with mushrooms often begin to wilt before harvesting. If, after it, they are stored in conditions of humidity higher than permissible, white bloom and small white tumors will begin to appear on the carrots. Also, ulcers will begin to appear at the root, as if covered with cracks. The entire root crop will be covered with a dry film, after which it is completely colored in a white-pinkish color. As the disease progresses, the spots will grow and become covered not only with cracks, but also with folds. When cutting the root crop, it will be possible to clearly trace where the border between healthy and infected tissue passes. Also, sometimes cavities can form inside the root crop.
At the last stages of storage, nothing remains alive in carrots.It becomes completely dry, covered with sores and rot of various sizes. This is also sometimes called dry rot, which is caused by more than one pathogen. Such a state of carrots can only mean that many diseases have settled in it. In such a situation, with high humidity, root crops can completely turn brown-brown and become covered with wet rot, completely erasing the border between healthy and infected tissue.
Disease control measures. The main way to protect your carrots from fusarium is the correct agricultural equipment, as always. It is very important to give your plants everything they need for proper growth and development, but at the same time, do not overdo it with care. You also need to remember to carefully examine the roots for unwanted infections and get rid of the infected as far as possible. In addition, remember that the soil in which your carrots grow is an equally important factor. Make it healthier and kill weeds in time.
Chemicals can also be used. For example, a drug called Fundazol helps to ensure the health and safety of the roots if they are immersed in a solution for a while.
Also, for the treatment of this disease in European countries, the medicine "Prozaro" is used, which is not registered in the Russian Federation as a medicine for carrots.
All these points must be observed, since fusarium is one of the most dangerous diseases that threatens your entire crop.
It is also necessary to closely monitor how healthy roots you send for storage, and get rid of infected ones in time.
And don't forget about good planting material, which is half the success of your future harvest.
Cercosporosis
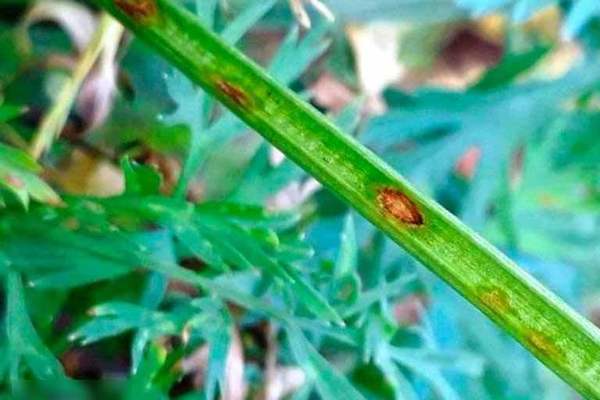

Description of the disease. Cercosporosis is a disease of carrots that causes multiple bright brown spots with a light center to appear on the leaves of the plant. The first spots are formed exclusively at the edges of the leaves, as a result of which they bend unnaturally. Over time, small spots coalesce into one large dark mass that completely covers the leaf. After this, spots begin to appear on the petioles of the leaf, hardening over time and turning into hard ulcers. They, like a ring, encircle the leaf and that, without the supply of nutrients, dries up and dies. After rain, in especially wet weather, the spots are covered with a gray "fluff".
Description of the causative agent of the disease. The fungus that infects carrots with cercosporosis is very fond of moisture, as well as a certain temperature: from 22 ° C to 27 ° C.
The fungus develops under such conditions in less than a week: in just 4 days, after which infection and disease begins. The pathogen spreads through the air or through water. It is especially necessary to closely monitor plant residues after harvesting, because it is in them that a mushroom can hide unnoticed for a long time and infect future crops.
Protective measures against disease. Your experience = the health of your crops. The more correct your agricultural technique, the less often your carrots will get sick with cercospora. Also, some hybrid varieties are resistant to this fungal disease. However, if the illness is serious, a drug called Kwardis should be used.
Diseases of carrots

