Alternaria: treatment of vegetable, berry, fruit crops
Content:
The article presents the disease Alternaria: treatment and description of the disease that affected vegetable, fruit, berry crops.
Alternaria: treatment, basic information about this disease
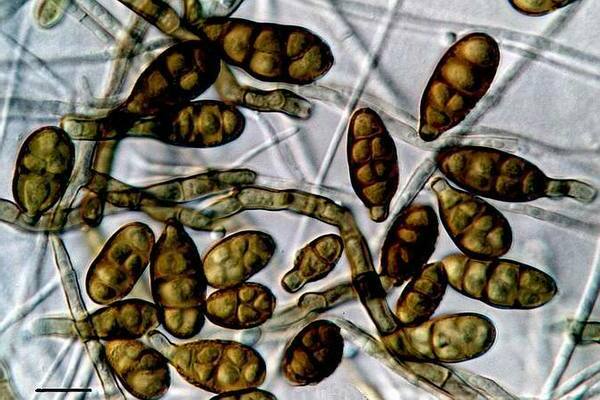
Alternaria: treatment
This disease is provoked by the fungal organisms "Alternaria". These microorganisms infect most of the various representatives of herbaceous crops. To save your plants, you need to know how to treat this disease. This information is presented at the end of this article.
However, for a start, it is worth being able to distinguish this fungal disease from other diseases that also appear on grassy ones as mold and spots. Depending on the specific plant, the signs of this disease may differ slightly, however, the methods of combating the disease are the same for all representatives of herbaceous crops.
Note!
This disease is dangerous because its spores are accelerated by wind, raindrops and parasites / insects to unharmed grassy ones. The disease can kill about fifty percent of the harvest of vegetables and fruit crops in three months.
Alternaria: treatment of this disease on tomatoes
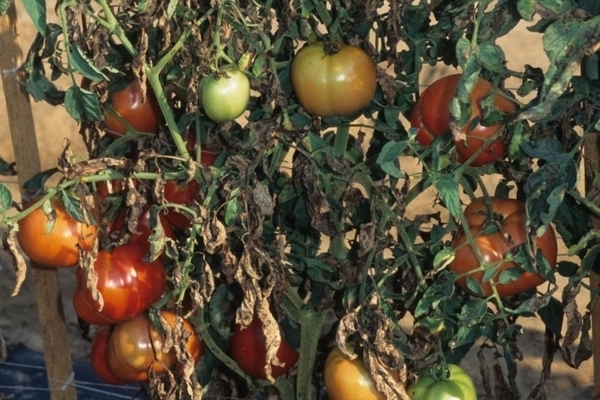

Alternaria: treatment
In tomatoes, this disease is often called "dry spotting", or "zonal spotting". The disease is harmful to all kinds of nightshades on a level with late blight, but it begins to appear rather faster: immediately after planting tomato planting material in fresh air or in a greenhouse.
Fungal disease infects all aerial areas of the herbaceous: foliage, stems and crops. The most important symptom of the disease is the formation of dried, pronounced circular spots (ranging from two millimeters to a couple of centimeters), gray and brownish at the same time. The infected foliage turns yellow ahead of time and falls off. If spots are deep enough, the herbaceous ones die. The crop is obtained with poor taste and an unpleasant appearance.
Hot and dry days with night dew and short rains are especially beneficial for the development of this disease. Unfortunately, there are no types and breeding varieties of tomatoes with a high level of resistance to this disease. Only some of them fall ill with Alternaria quite rarely, for example, the "F1 firebird". Treatment is recommended with the help of specialized drugs, activities that are described at the end of the article.
Alternaria potato: photo, description
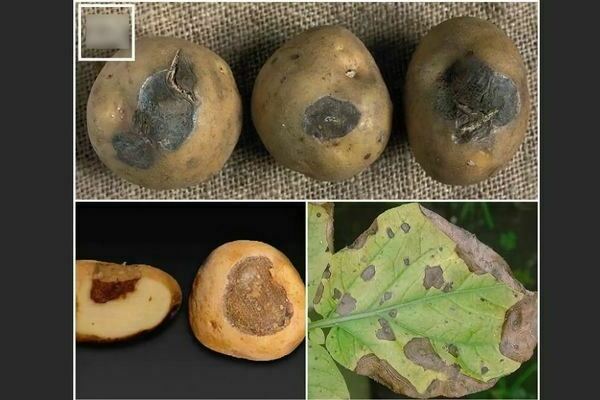

Alternaria potato: photo
On potatoes, this disease usually appears from the second week of the first summer month (about two to three weeks before the flowering process) and does not allow the herbaceous to rest until the autumn season. The disease especially prefers varieties with medium to medium and late ripening.
To begin with, foliage and stems are damaged (dried round spots of brownish color appear on them), as a result of this, the growth rate of potatoes decreases.Tubers are damaged, usually during the harvesting process, when they come into contact with the spores of the fungus placed on the tops, or when the shell is mechanically damaged. Tubers form faint spots on themselves.
Note!
The following varieties have a fairly high level of resistance to this disease:
- "Dolphin".
- "pace".
- "Dina".
- "belongings".
- "resin".
- "lugovskaya".
- "lapis lazuli".
Alternaria grape photo, description
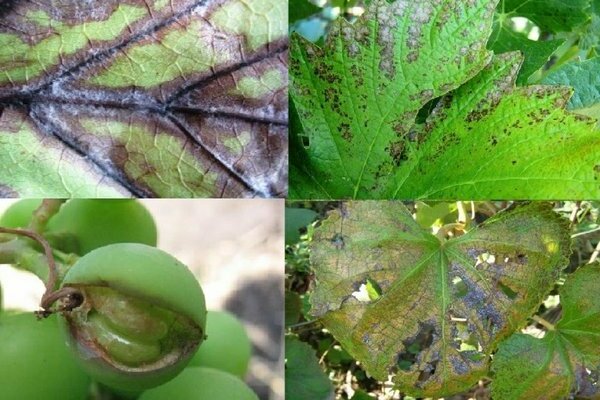

The first signs of the disease are formed at the end of the spring season. Infected foliage and shoots of grapes have light yellowish and grayish spots, which are not difficult to confuse with oidium disease. Over time, the spots turn black and form brownish spots. With severe infection, the foliage darkens and dries out.
On fruits, the disease appears as a pale silvery gloss on the shell; over time, a dark grayish coating of the fungus develops. The fruit shrinks and tastes unpleasant.
Apple Alternaria
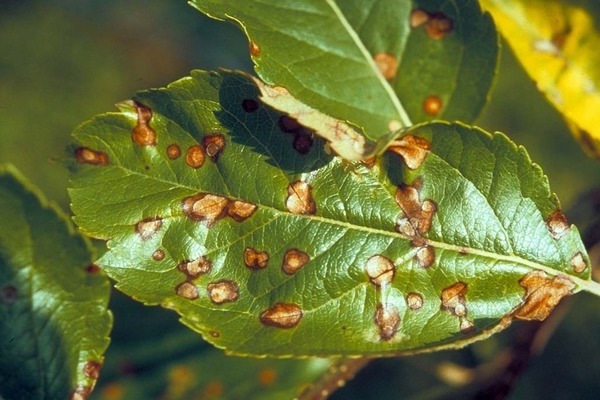

At the end of the spring season and at the beginning of the summer season (most often thirty days after the flowering process), small round specks of brownish color with purple edging are formed on the foliage of a fruiting tree. After a while, the spots grow, and sometimes merge. Infected foliage falls prematurely. This disease also infects the crop: small, non-dark spots with a blackish border are formed on it.
This disease on cabbage, or the disease "black spot"
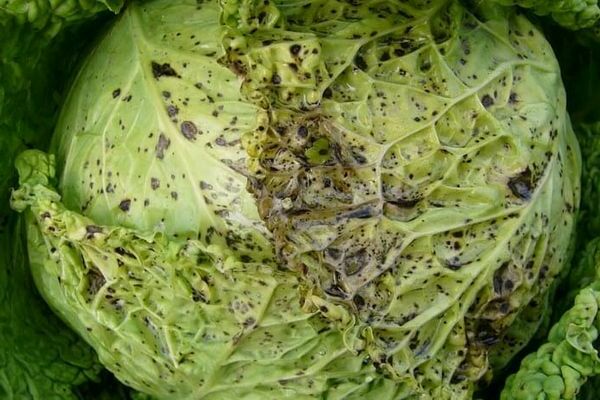

The disease infects old and young herbaceous varieties of cabbage. Dark necrotic stripes and spots appear on the planting material (seed lobes and hypocotal knees), as a result of which the herbaceous dies. In old cabbage, black specks appear on the top foliage of the head of cabbage, covered with a loose layer of soot-colored bloom. In this case, the spots usually have a yellowish border.
With the formation of this disease, "brown rot" begins to develop on cauliflower and its flowers, as a result of which the herbaceous plant becomes prohibited for inclusion in your diet.
This disease on pepper
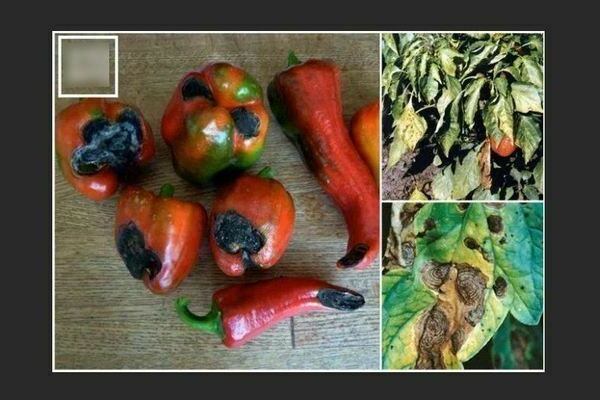

On the foliage of the pepper, specks are formed in the corners, with veins along the edges, of a dark brownish or dark color. After a while, the specks move to the crop. To begin with, they are watery, after a while they turn black, and in the middle a rather light color appears and are covered with a blackish bloom of mold.
This disease on onions
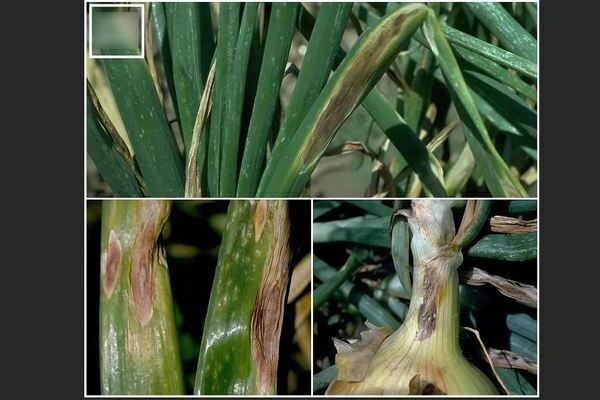

For a start, small watery specks with a snow-white center appear on the foliage of the onion. Then they grow, turn black and brown and reddish color appears. After a while, the specks merge, after which the foliage breaks off and dies. Under the condition of an excessive amount of moisture, a gray and blackish coating forms on the specks.
The bulbs are also susceptible to this disease. Infected tissues are watery to begin with, then turn yellow or greenish, a brown coating forms between the scales.
Note!
This disease can also be found on cucumbers, barley, carrots, peas, pears, sunflowers, wheat, tobacco and gooseberries. And from flowers, the disease attacks dracaena, orchid and zinnia.
Alternaria: treatment
When the first symptoms of the disease form, the herbaceous ones are treated with the preparation "copper sulfate" (twenty grams of solution and two hundred grams of crushed laundry soap per ten liters of liquid) or other fungicidal preparations (means "abiga-peak", "ridomil golden mts", "bravo" , "Poliram", "kvadris"). The treatment is carried out with a time interval of one to two weeks until the symptoms of the disease are relieved.
Experienced summer residents who do not like chemical preparations are advised to arrange the prevention of this disease with the help of this biological agent, for example, "trichodermin".They also process the foliage and stems of herbaceous plants in the second - third spring month for the prevention of disease.
Remember: the infected tops of representatives of herbaceous crops are removed no later than seven days before harvesting, so that the spores of the fungus do not have time to pass to the crop.
The fight against this disease is sometimes effective, which means that it is necessary to remember about preventive procedures. To prevent disease, seeds or seedlings are treated with fungicidal preparations. To increase the immunity of herbaceous plantings, they are sprayed a couple of times in three months with the drug "immunocyte": one tablet is placed in one tablespoon of liquid and two liters of water are poured out. The drug will be enough for you for fifty square meters.
It is necessary at the right time to fight parasites, especially aphids, because it can transfer fungal diseases to unharmed herbaceous plants. And also to remove and destroy all the herbaceous waste of affected plants, in the autumn season to dig deep into the ground and strictly follow the crop rotation.
Alternaria: treatment

