Quince (Japanese Henomeles)
Content:
Japanese quince is also often called Japanese henomeles. This plant loves warm growing conditions. This culture shows good results on the territory of regions where a mild climate prevails. If you want to plant a quince in an area where winters are rather harsh, then keep in mind that this plant can withstand a drop in temperature to -30 degrees.
However, at the same time, young stems that are above the snow cover may freeze slightly. The same goes for quince flower buds. Thus, the flowering becomes less lush. And the part of the plant, preserved under the snow, can begin to bloom in the spring.
Japanese quince: landing. Choosing a place
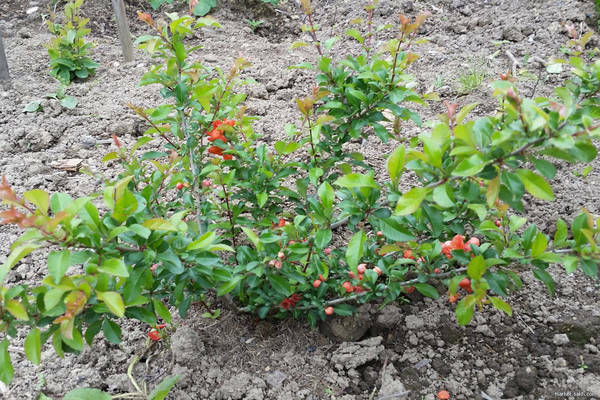

Chaenomeles Japanese loves a lot of light, so you need to choose a well-lit land for planting. If you plant a quince in a shaded area, then the development of plants will proceed slowly, and this may not be the best way to affect flowering.
Japanese quince is very well able to withstand dry weather. Moreover, when the plant is still too young, you need to moisten the soil from time to time. At the same time, water should not stagnate.
Quince feels best on loose soils. Sandy loam soil, loam, sod-podzolic soil are well suited. At the same time, the soil should be well fertilized, contain a lot of humus. The acidity level should be low, around 6.5 units. Not the best option for chaenomeles would be a soil that contains a lot of peat.
If this crop is placed in an area where there is too much alkali, then there is a risk that the plants will develop chlorosis of the foliage. When selecting a site for planting quince, it is best to give preference to land with a southern exposure. The area where the quince will grow should be well protected from gusty winds and low temperatures. If you have
not in a flat area, but in a hilly area, plant Japanese chaenomeles on the southern or southwestern slope.
How to prepare a plot and plant a quince
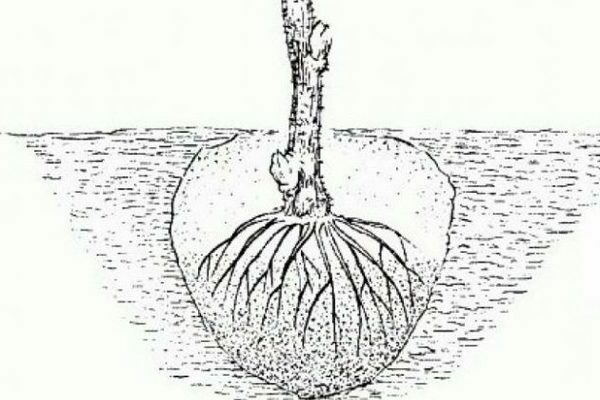
Planting scheme of Japanese quince
If you plan to plant a quince in the spring, then you need to prepare the site in advance, preferably in the fall. If there is a lot of weed growing on the site, then it must be completely removed, and the soil must be kept fallow until the onset of the planting period. And if the soil contains too few nutrients, and also has a heavy structure, then you need to add sand (one part) and leafy earth (two parts).
In addition, you need to add additional fertilizers, both organic and mineral. For these purposes, you can use compost, which consists of peat and manure. One square of the area accounts for about ten kilograms of such fertilizer. In addition, you need to make top dressing containing phosphorus and potassium.
For one square meter, mineral fertilizers are applied in an amount of about forty grams. Such dressings need to be applied to a depth of ten to fifteen centimeters. Thus, the soil will become lighter, moisture and oxygen will pass better.
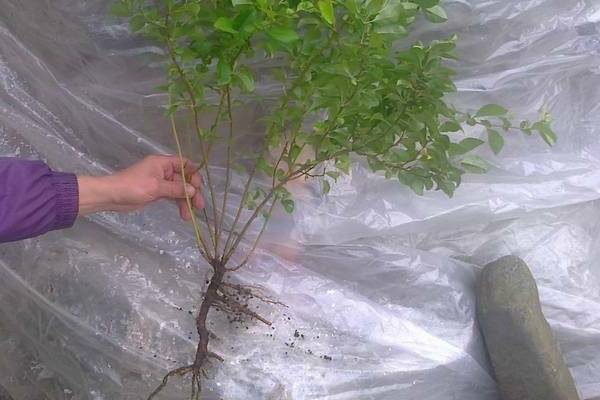

If the seedlings have an open root system, then it is better to plant such a plant in a permanent habitat in the spring.This is usually done after the ground has completely thawed, and the buds have not yet begun to bloom.
In the autumn, you can also plant quince, this is done after all the foliage has already fallen. However, spring planting is more preferable, because the plant is quite demanding for warm conditions, and there is a risk that before the onset of cold weather the seedling simply will not have time to take root and the plant will die.
When choosing planting material, it is better to give preference to seedlings that are already two years old. In this case, the root system must be of a closed type. If you are planting a single plant that is three to five years old, you need to dig holes for planting, the diameter of which should be up to fifty centimeters.
The depth can vary from fifty to eighty centimeters. The pits need to be filled with a fertilizer mixture, which will consist of a couple of buckets of humus, as well as mineral dressings. Superphosphate (three hundred grams), potassium nitrate (thirty grams), wood ash (five hundred grams) are good for this.
This crop can be planted in small group compositions. With the help of quince, you can refine the fence or garden paths. Quince can be a good "living fence".
A certain distance must be maintained between the plants, about fifty to sixty centimeters. If the plants are planted as part of the composition, then between crops should be eighty to one hundred centimeters.
The root collar of this crop should be flush with the ground when planting. The root system should not be exposed, that is, the root collar should not be located higher than the ground level.
It should also be noted that the root collar should not go underground. This will make the shrub grow and develop too slowly.
When growing Japanese quince, one must take into account the fact that this culture reacts very negatively to transplants. Therefore, the choice of a site for planting must be taken seriously.
It is necessary to choose a permanent habitat so that the plants are not injured by transplants to another site. In the same place, this culture can successfully grow for fifty to sixty years.
Japanese quince: care
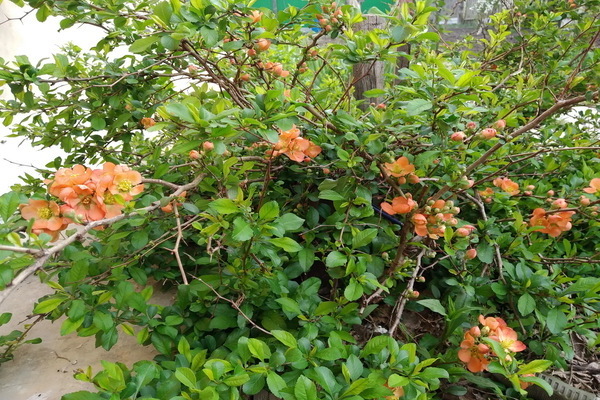

In order to have more flowers on your shrubs, in the summer you need to spend loosening near-trunk zone of shrubs. This is not done too deeply, about eight to ten centimeters. In addition, this procedure is recommended to be combined with the removal of weeds from the site.
To simplify your task, you can stack in the trunk circles mulching a layer three to five centimeters thick. For these purposes, you can use peat, sawdust, nutshells, crushed bark. It is best to lay the mulching layer at the end of spring. At this time, the soil is still well saturated with moisture and warmed up.
In the autumn, you can start laying mulch after stable low temperatures. A layer of mulch should cover the soil around the circumference of the shrub, or it can be fifteen to twenty centimeters more.
For the first year, after the plant has been planted, add additional fertilizers there is no need in the soil, since there is a risk that the still young and weak root system will receive burns. The nutrients that were laid in the planting pits are quite enough for the first time.
In the second or third year after the plant has been planted, the Japanese quince must be fed with organic and mineral fertilizers. This procedure is done, as a rule, after the snow cover has melted.
For this purpose, the following is introduced into the zone of the near-stem circles of plants: compost (one bucket), superphosphate (three hundred grams), potassium dressing (one hundred grams).Liquid fertilization is recommended throughout the summer season.
For this, ammonium nitrate is well suited (consumption is about twenty grams per plant). Poultry droppings will also cope well with this task, one plant accounts for three liters of a ten percent solution.
So that your Japanese quince is not damaged in the winter, in late autumn you need sprinkle plants with leaf litter, or use spruce branches for this. This measure is mandatory for both young plants and older shrubs.
Saplings, cuttings that are sent for wintering also need additional insulation. For this, materials such as spunbond and lutrasil can be used. If you have a not too tall and compact variety of quince, then you can use boxes made of wood or cardboard for this.
How Japanese quince reproduces using seeds
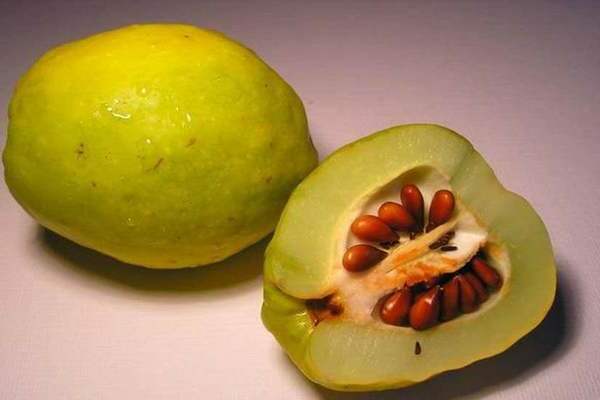

This method of reproduction of quince among lovers of this culture is the simplest and most reliable. To get seed, you need to use well-ripened fruits that are ready to be harvested and processed.
The seeds inside the fruit should be brown, they are carefully removed and used for further planting. Seed material is removed and planted at the same time, in the fall. The so-called "winter sowing" is carried out. The seeds of this culture have a high germination rate, about eighty percent.
Plants sprout quite amicably and densely in the spring. It should be noted that the success of seedlings does not depend on the structure and composition of the soil used.
If for some reason you do not have time to plant the seeds within the given timeframe, then they will need to be laid on stratification. For this purpose, the seeds are kept in wet sand for two to three months. In this case, the temperature regime should be observed at the level of +3 +5 degrees.
When the first shoots appear, the seedlings should move to the site in the spring. The sprouts, which have already turned two years old, have an elongated root system in the form of a rod, and if the plant is not transplanted too carefully, the rhizome can be injured, which can subsequently lead to the death of the plant. To prevent this from happening, it is recommended to transplant seedlings to a permanent habitat at the first opportunity.
Cuttings and propagation by grafting

Reproduction by vegetative methods of Japanese chaenomeles is economically not as efficient as seed propagation. However, among the advantages of reproduction of quince with the help of grafting or cuttings, the preservation of the varietal trait of the plant can be called.
Cuttings are usually harvested in early June. For this, the weather must be dry and not too hot. Slices should be cut early in the morning. Each cutting should have from one to two internodes.
The best results in terms of similarity are shown by those cuttings on which there is some wood from last year. One centimeter of last year's bark will be enough.
For the best result, you need to use root growth stimulants. To do this, you can use Kornevin, or soak the roots in a solution of indolyl butyric acid for a day.
Cuttings are planted at an angle. For this, a mixture is used that includes sand (three parts) and peat (one part). As for the planting scheme, the cuttings are placed with the calculation of seven centimeters by five. If the temperature outside is from +20 to +25 degrees, then the cuttings can take root after thirty-five to forty days. Special drugs that stimulate root growth increase the likelihood of survival by ten to twenty percent.
As for the method of reproduction by grafting, it is carried out, as a rule, in the spring, in May. For this, a varietal cutting and a young plant of Japanese quince are used.To inoculate a plant by the "eye" method, that is, by budding, the scion (varietal cuttings) must be prepared in the second half of summer, when the second sap flow occurs.
To this end, from the center of the cutting, using a well-sharpened special knife, you need to cut off the kidney along with part of the wood. A "T" cut must be made on the wood of the rootstock used. The edge of the cut must be folded back and a bud with a piece of bark must be inserted under the wood. Next, you need to firmly press these parts of the quince, tie and process with a garden varnish.
After three to four weeks, you can estimate how the “eyes” were able to take root. In the spring period next season, in case of successful survival of the bud and the appearance of a new stalk, the bandage can be removed.
On a compact, not tall quince shrub, two buds are usually grafted, which are located opposite. In addition, several related plants can be used. For example, pear or hawthorn.
Quince varieties with beautiful flowers, which are grafted onto a frost-resistant stem, look quite unusual. For the stock, you can use a wild pear at the age of three years, hawthorn, spiked irga, mountain ash.
Since varietal quince does not tolerate low temperatures very well, the graft should be located closer to the soil level, at about a height of sixty to ninety centimeters. This will reduce the risk that the plant will suffer during wintering. If budding is carried out correctly, then the probability that the eyes will take root varies from fifty to eighty percent.
Each season it is necessary to form the crown of the plant. Shoots that form below the site where the vaccine is located should be removed from time to time. To make the standard plant more stable, it must be tied to a peg. It will not be superfluous if you install an additional support under the too elongated quince stems.
It is worth remembering that the standard form of the Japanese quince does not tolerate low temperatures very well in winter, so such plants should be planted in an area protected from winds. In addition, the plants need to be additionally insulated during the cold season.
How Japanese quince reproduces using root suckers

This culture tends to form a large number of root shoots. Because of this, the shrub actively grows in breadth. When a plant is about twenty years old, it can occupy an area of up to two square meters.
Thanks to the many such shoots, the root system of this crop can securely hold the soil in the hills. The roots branch strongly underground and have an elastic structure. Therefore, when uprooting an adult plant, some difficulties may arise.
During the extraction of basal shoots, you need to select stems that have grown ten to fifteen centimeters in length and have a thickness of about half a centimeter. In this case, the root system should be well developed.
Shoots should be planted vertically and watered from time to time. The soil moisture level should be maintained constantly, while there should be no stagnation of water. After moistening the soil, a mulching layer is laid along the perimeter of the plant. For this, humus, shavings or chips are well suited.
The main disadvantage of this method of reproduction of quince is an insufficiently developed root system in some shoots, so that the planting material is often sent for growing. Some gardeners note that at first such seedlings give too small fruits.
About the correct pruning of quince
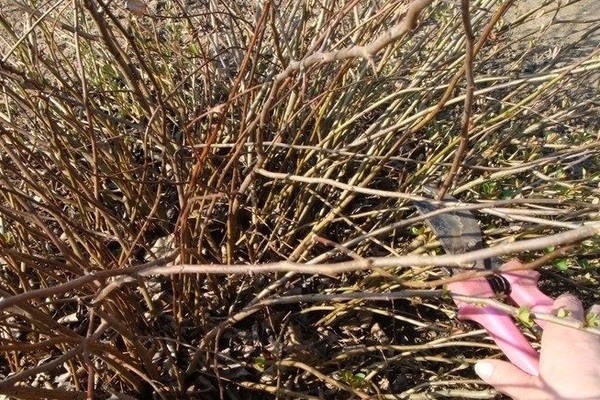

This crop reacts very positively to timely pruning. However, the presence of sharp thorns on the shoots makes this procedure not very pleasant and rather troublesome. It is best to use elongated thick gloves for these purposes, the so-called garden leggings.In them, your hands will be protected from thorny quince branches.
In the spring, this crop must be pruned for sanitary purposes. During this event, all dried branches are removed, as well as those shoots that are frozen in winter. To make pruning less painful for plants, you need to use a well-sharpened pruner or saw.
Where the cut was carried out, it is necessary to process it with a garden varnish. Quince is quite good at recovering after dry and broken shoots have been removed.
In addition to sanitary pruning, it is necessary to periodically carry out formative pruning. It is carried out at the beginning of the spring period for plants that are already four to five years old. So that the quince does not grow too actively in the area, as well as to avoid thickening of the crown, every year it is necessary to partially remove the root shoots. A maximum of two to three root shoots should be left.
The offspring, which grow horizontally and are located twenty to forty centimeters from the ground level, are of the greatest value. Offshoots that are parallel to the ground in close proximity to the ground must be removed. The same goes for stems that grow vertically.
In addition to the above scraps, periodically you need to carry out anti-aging pruning. This event is carried out with plants that are eight to ten years old. If the annual growth of shoots began to be a maximum of ten centimeters, then this is a sure sign that it is time to rejuvenate the shrub.
To begin with, the plant must be thinned out, all weakened, too thin and long shoots are removed. You need to leave from ten to fifteen of the most powerful stems. Since the main part of the fruits is formed on three-year and four-year-old branches, the formation of a plant should also consist in their preservation and removal of shoots that are more than five years old.
What is the disease of Japanese quince and the main pests of the plant

This culture is almost not attacked by harmful insects. If the weather is humid and cool, then there is a risk that various spots and necrosis may appear on the foliage and the fruits themselves.
If the plants are "wielded" by diseases of fungal origin, then, as a rule, deformation of the leaf plates occurs. Over time, the foliage dries up.
A common Japanese quince disease is ramulariasis. In this case, spots of a brown hue appear. Cercosporiasis - also a common problem that occurs on quince plantings. With this disease, spots of brown color and round shape appear. After a while, these spots begin to fade.
To effectively solve the problems associated with fungal diseases, it is best to spray the bushes with special preparations. Fundazole solution is well suited for this. Copper sulfate with the addition of a soap solution can be used for the same purpose. There are about one hundred grams of vitriol per ten liters of water. This procedure is performed before the leaves begin to unfold.
You can also use folk methods, for example, onion infusion. For these purposes, juicy onions (three hundred grams) or husks (one hundred fifty grams) are taken. This amount is enough for ten liters of water. Infusion lasts about a day. Then the infusion must be filtered and sprayed over the summer period at intervals of five days.
Japanese quince - fruits. How to collect and save
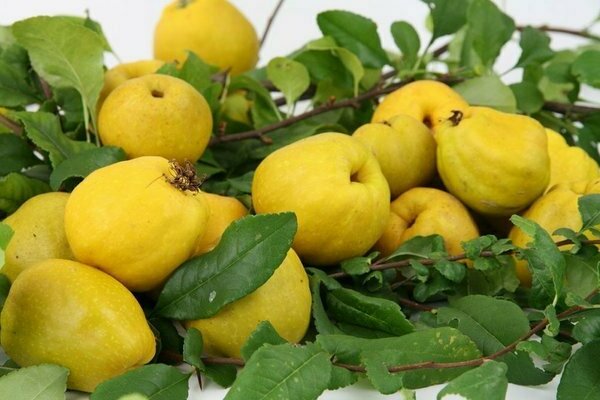

Ripening of Japanese quince fruits occurs in late autumn, in the last days of September - in October. From one plant, you can get from one to two kilograms of fruit. If all the rules for growing and agricultural technology are followed, three kilograms of fruit can be removed.
Pollination of Japanese chaenomeles is carried out crosswise.To get a decent harvest, you need to plant two or three varieties of Japanese quince in the immediate vicinity.
In the middle zone, especially if there is too much rain and cold in the summer, the quince does not ripen too well, and the fruits hang green on the branches for a long time. The fruit must be fully harvested before the cold weather sets in.
Those fruits that have been exposed to frost begin to fall off quickly, the quality of taste and aromatics drop sharply. The quince becomes too soft and watery. There is little point in processing or storing such fruits.
Quince is quite capable of ripening when harvested. Room conditions are fine for this. During storage, the fruits gradually turn yellow. Sometimes the quince begins to frown, while the putrefactive processes do not begin.
Such fruits can also be successfully processed. If you observe a temperature regime of about +2 degrees and maintain high air humidity, then the fruits can retain their qualities until December and even until February.
How Japanese quince is used
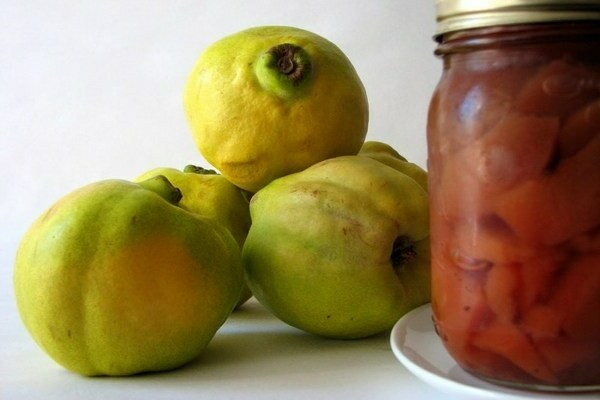

This culture bears quite aromatic fruits that can be used to prepare a wide variety of dishes and preparations. Quince fruits can serve as a good base for tea, jams, marmalade, compote, distillate or liqueur.
Quince makes delicious jelly, marshmallow, syrup, jam. Quince can be a good addition to apple compote, and the data goes well with chokeberry (chokeberry), peaches and apricots.
If you follow the basic principles of growing and caring for this crop, then the result will not be long in coming. A good harvest of unusual fruits will delight you and your family from year to year.

