Agricultural technology for growing potatoes.
Content:
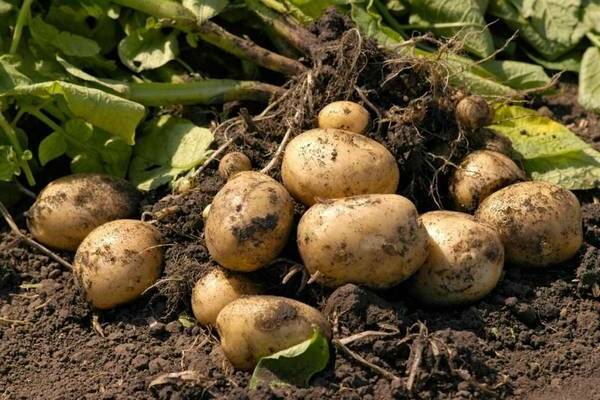

Many summer residents grow potatoes on their site. It is no secret that it appeared in our country in the 18th century. It was first grown as an ornamental plant. Then the peasants for a very long time did not agree with the decrees of the government and staged potato riots in protest against the cultivation of this crop. But now potatoes are grown in almost every home. Everyone loves this crumbly and yellow, and also nutritious vegetable. However, it also requires special care. Therefore, it is necessary to follow certain rules when growing this type of crop.
We plant potatoes - what kind of soil should be.
Potatoes love loose, fertile, breathable and light soil. However, this culture does not have fundamental requirements for the composition of the soil. For growing potatoes, it is recommended to use potash-phosphorus fertilizers, as well as to apply manure for winter plowing. In the spring, the soil is cultivated by softening the top layer and breaking pebbles. Fertilizer is usually mixed with soil and applied to the holes.
Choosing potato varieties.
Any agronomic measure begins with the choice of a variety. First of all, it must be adapted to those natural-geographical, climatic conditions that are typical for a given area. It is recommended not to grow potatoes in the same place for several years in a row, so you need to do crop rotation in a timely manner. It is recommended to apply manure in the fall, consuming about 20 tons of organic fertilizer per hectare of land. Sometimes, in the fall, they sow greenery in order to plow the area before winter and enrich the land with green fertilizer. Sometimes organic products are used together with mineral fertilizers. You should also be aware that potatoes do not like calcium, so do not add it to the soil.
We feed potatoes with other means.
Before plowing, it is recommended to apply phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and compost. This loosens the soil, structures the soil and enriches it with the necessary nutrients. Magnesium ensures that your plants are resistant to various diseases. And potassium increases the starch content in tubers. It is better not to add nitrogenous fertilizers that reduce the yield of potatoes.
Features of care.
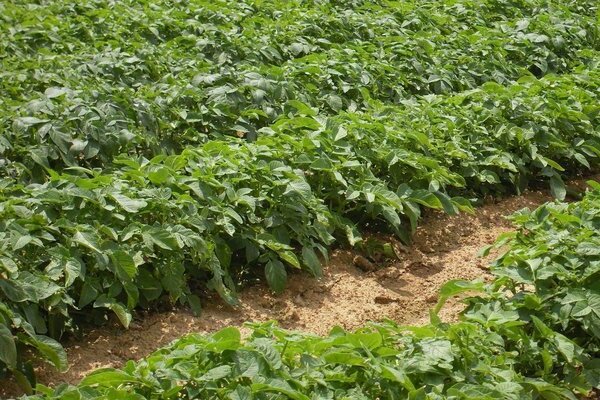

Potatoes are planted in furrows, in holes. If you are planting potatoes in a mechanized way, then you can either ask farmers for help using a tractor with a potato planter, or ask someone to make furrows for you on a walk-behind tractor or tractor. Then you can independently throw the potatoes into the sealed beds, and manually cover the potatoes with soil. You can plant this culture just under a shovel. To do this, you need to correctly maintain the distance between the plants and, at the same time, adhere to strict geometry, so that you can in the future, in a mechanized way, produce hilling of potatoes. Also, even ridges are needed so that it is easier for you to process and weed the site yourself. Believe me, in one summer-spring season you will more than once weed aisles, process potatoes from pests, and therefore walk along these very even beds.
Diseases.
Potatoes also suffer from fungal, viral and bacterial diseases, therefore, already at planting, tubers are often treated for many diseases. Most often, potatoes do not suffer from any diseases, but sometimes they are treated with fungicides for prevention.With regards to pests, it should be said that the Colorado potato beetle is considered the most dangerous. It is also fought with using a wide variety of methods, ranging from manual collection of adults to chemical treatment. Sometimes potatoes should be treated for aphids, for this they use insecticides. In conclusion, I would like to note that the potato as a whole is not a very whimsical Culture. However, it must be planted on time, carefully treated against pests, weeded and fed. Therefore, do not leave potatoes to their fate and often look under the leaves in order to notice pests, weeds or signs of any diseases in time.

